Antibody Pair for Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 Ligand 1 (PDL1)
CD274; PDCD1LG1; B7-H; B7H1; PD-L1; PDCD1L1; PDCD1-LG1; Programed Death Ligand 1
- Product No.PSA788Hu01
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
-
Reagent Contents
Recombinant Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 Ligand 1 (PDL1) 50ug Standard Polyclonal Antibody to Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 Ligand 1 (PDL1) 200ug Capture Ab Biotin-Linked Monoclonal Antibody to Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 Ligand 1 (PDL1) 10ug Detection Ab - ApplicationsELISA; CLIA; ELISPOT; Luminex; Immunochromatography and other Immunoassays.
- DownloadInstruction Manual
- UOM 96T*596T*10 96T*20 96T*50 96T*100
- FOB
US$ 851
US$ 1418
US$ 2552
US$ 4963
US$ 8508
For more details, please contact local distributors!
MATCHING TESTS
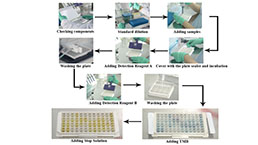
USAGE
STORAGE
Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8°C for one month. Aliquot and store at -80°C for 12 months.
STABILITY
The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37°C for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
GIVEAWAYS
INCREMENT SERVICES
| Magazine | Citations |
| Chinese Journal of Cancer | Level of circulating PD-L1 expression in patients with advanced gastric cancer and its clinical implications NCBI: PMC3937742 |
| Leukemia.? | High level of soluble programmed cell death ligand 1 in blood impacts overall survival in aggressive diffuse large B-Cell lymphoma: results from a French multicenter clinical trial. Pubmed:24732592 |
| Diabetes?Metab Res Rev. | PD‐L1 gene polymorphisms and low serum level of PD‐L1 protein are associated to type 1 diabetes in Chile Pubmed:24816853 |
| Lancet Haematol | Ratios of T-cell immune effectors and checkpoint molecules as prognostic biomarkers in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a population-based study PubMed: 26686046 |
| Eur J Cancer. | High levels of the soluble programmed death-ligand (sPD-L1) identify hepatocellular carcinoma patients with a poor prognosis. Pubmed:27039170 |
| Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology | Serum levels of soluble programmed cell death ligand 1 as a prognostic factor on the first-line treatment of metastatic or recurrent gastric cancer article:10.1007 |
| Journal of Hematology & Oncology | PD-L1 is upregulated by EBV-driven LMP1 through NF-κB pathway and correlates with poor prognosis in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma pubmed:27737703 |
| Lung Cancer. | High plasma levels of soluble programmed cell death ligand 1 are prognostic for reduced survival in advanced lung cancer. pubmed:28212990 |
| Oncotarget | Soluble programmed death-ligand 1 (sPDL1) and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) predictssurvival in advanced biliary tract cancer patients treated with palliative chemotherapy. pubmed:27780932 |
| Oncotarget | High post-treatment serum levels of soluble programmed cell death ligand 1 predict earlyrelapse and poor prognosis in extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma patients. pubmed:27105512 |
| Oncotarget. | Soluble PD-L1: A biomarker to predict progression of autologous transplantation in patients with multiple myeloma pubmed:27566569 |
| Cancer Immunol Immunother. | Programmed death-ligand 1 and its soluble form are highly expressed in nasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma: a potential rationale for immunotherapy. pubmed:28349165 |
| Leukemia | Soluble programmed death-ligand 1 as a prognostic biomarker for overall survival in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a replication study and combined analysis of 508 patients leu2016385a |
| Medicine | Plasma levels of soluble programmed death ligand-1 may be associated with overall survival in nonsmall cell lung cancer patients receiving thoracic radiotherapy. pubmed:28207525 |
| Allergology International | Inverse correlation of soluble programmed cell death-1 ligand-1 (sPD-L1) with eosinophil count and clinical severity in allergic rhinitis patients pubmed:27617656 |
| Medicine | Plasma levels of soluble programmed death ligand-1 may be associated with overall survival in nonsmall cell lung cancer patients receiving thoracic radiotherapy PMC5319514 |
| American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine | Soluble Programed Death Receptor 1 Ligand (sPD-L1) in Pleural Fluid of Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma (MPM) Pdf:10.1164 |
| Clinical Lung Cancer | Soluble Programmed Cell Death Ligand 1 as a Novel Biomarker for Nivolumab Therapy for Non–Small-cell Lung Cancer Pubmed:29859759 |
| Journal of Rheumatology | Increased levels of soluble programmed death ligand 1 associate with malignancy in patients with dermatomyositis Pubmed:29419471 |
| Translational Oncology | High Serum Level of Soluble Programmed Death Ligand 1 is Associated With a Poor Prognosis in Hodgkin Lymphoma Pubmed:29698935 |
| Immunology Letters | Increased levels of soluble co-stimulatory molecule PD-L1 (B7-H1) in the plasma of viraemic HIV-1+ individuals Pubmed: 30236481 |
| Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology | Pre-treatment serum levels of soluble programmed cell death-ligand 1 predict prognosis in patients with hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma Pubmed: 30267213 |
| Annals of Surgical Oncology | Soluble PD-L1 Expression in Circulation as a Predictive Marker for Recurrence and Prognosis in Gastric Cancer: Direct Comparison of the Clinical Burden Between … Pubmed: 30565045 |
| American Journal of Reproductive Immunology | Identification of programmed cell death 1 and its ligand in the testicular tissue of mice Pubmed: 30578744 |
| PLoS One | Clinical significance of soluble programmed cell death-1 and soluble programmed cell death-ligand 1 in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer treated … Pubmed: 30807610 |
| Endocrine Connections | Elevated levels of soluble PD-L1 are associated with reduced recurrence in papillary thyroid cancer Pubmed: 31252406 |
| Scientific Reports | Prognostic implications of soluble programmed death-ligand 1 and its dynamics during chemotherapy in unresectable pancreatic cancer Pubmed: 31366979 |
| Critical Reviews in Oncology / Hematology | The Clinical Significance of Soluble PD-1 and PD-L1 in Lung Cancer Pubmed: 31675543 |
| PLoS One | Clinical implications of APOBEC3A and 3B expression in patients with breast cancer Pubmed: 32176735 |
| Cancers | Predictive Value of Soluble PD-1, PD-L1, VEGFA, CD40 Ligand and CD44 for Nivolumab Therapy in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Case-Control Study Pubmed: 32085544 |
| Serum levels of soluble programmed death-ligand 1 (sPD-L1) in patients with primary central nervous system diffuse large B-cell lymphoma Pubmed: 32054467 | |
| LIVER INTERNATIONAL | The prognostic role of soluble transforming growth factor‐β and its correlation with soluble programmed death‐ligand 1 in biliary tract cancer Pubmed: 32780918 |
| CANCER IMMUNOLOGY IMMUNOTHERAPY | Prognostic impacts of tumoral expression and serum levels of PD-L1 and CTLA-4 in colorectal cancer patients Pubmed: 32577816 |
| Soluble PD-L1: a potential immune marker for HIV-1 infection and virological failure Pubmed: 32443313 | |
| Cancer Immunol Immunother | The clinical implication of soluble PD-L1 (sPD-L1) in patients with breast cancer and its biological function in regulating the function of T lymphocyte 33688997 |
| Acta Biochim Biophys Sin | Prognostic prospect of soluble programmed cell death ligand-1 (sPD-L1) in cancer management 34180502 |
| EMBO J | Microglial PD‐1 stimulation by astrocytic PD‐L1 suppresses neuroinflammation and Alzheimer's disease pathology 34825707 |
| Mol Pharm | A Novel Small Cyclic Peptide-Based 68Ga-Radiotracer for Positron Emission Tomography Imaging of PD-L1 Expression in Tumors 34910492 |
| Mol Hum Reprod | Macrophage Associated Immune Checkpoint CD47 Blocking Ameliorates Endometriosis Pubmed:35404426 |
| Journal of Nanobiotechnology | Microbial hydrogen “manufactory” for enhanced gas therapy and self-activated immunotherapy via reduced immune escape Pubmed:35705974 |
| Medicina | Assessment of the RANTES Level Correlation and Selected Inflammatory and Pro-Angiogenic Molecules Evaluation of Their Influence on CRC Clinical Features: A … Pubmed:35208526 |