Packages (Simulation)

Reagent Preparation
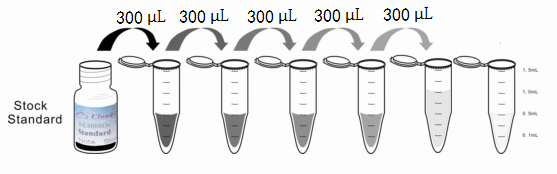
Image (I)
Image (II)
Certificate


Multiplex Assay Kit for Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 Ligand 1 (PDL1) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay)
CD274; PDCD1LG1; B7-H; B7H1; PD-L1; PDCD1L1; PDCD1-LG1; Programed Death Ligand 1
(Note: Up to 8-plex in one testing reaction)
- Product No.LMA788Hu
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
- Sample Typeserum, plasma, tissue homogenates and other biological fluids.
- Test MethodDouble-antibody Sandwich
- Assay Length3.5h
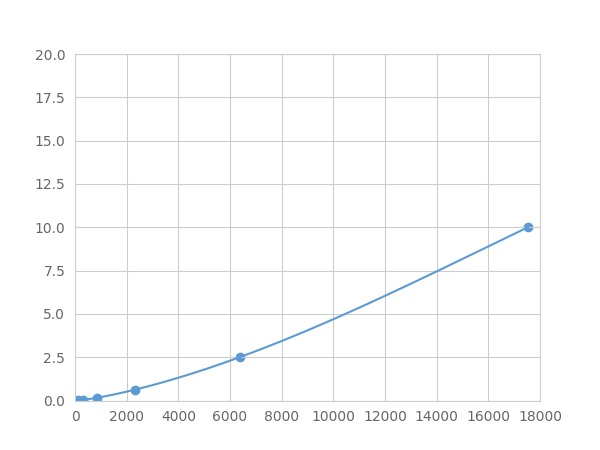
- Detection Range0.01-10ng/mL
- SensitivityThe minimum detectable dose of this kit is typically less than 0.003 ng/mL.
- DownloadInstruction Manual
- UOM 8Plex 7Plex 6Plex 5Plex 4Plex 3Plex 2Plex1Plex
- FOB
US$ 393
US$ 408
US$ 431
US$ 461
US$ 491
US$ 537
US$ 605
US$ 756
Add to Price Calculator
Result
For more details, please contact local distributors!
Specificity
This assay has high sensitivity and excellent specificity for detection of Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 Ligand 1 (PDL1) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay).
No significant cross-reactivity or interference between Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 Ligand 1 (PDL1) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) and analogues was observed.
Recovery
Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of recombinant Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 Ligand 1 (PDL1) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 Ligand 1 (PDL1) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) in samples.
| Matrix | Recovery range (%) | Average(%) |
| serum(n=5) | 87-101 | 92 |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 91-99 | 95 |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 80-90 | 86 |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 Ligand 1 (PDL1) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 Ligand 1 (PDL1) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) were tested on 3 different plates, 8 replicates in each plate.
CV(%) = SD/meanX100
Intra-Assay: CV<10%
Inter-Assay: CV<12%
Linearity
The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 Ligand 1 (PDL1) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| Sample | 1:2 | 1:4 | 1:8 | 1:16 |
| serum(n=5) | 86-99% | 85-99% | 93-101% | 78-104% |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 82-97% | 98-105% | 89-98% | 85-103% |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 78-95% | 90-99% | 90-101% | 98-105% |
Stability
The stability of kit is determined by the loss rate of activity. The loss rate of this kit is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
To minimize extra influence on the performance, operation procedures and lab conditions, especially room temperature, air humidity, incubator temperature should be strictly controlled. It is also strongly suggested that the whole assay is performed by the same operator from the beginning to the end.
Reagents and materials provided
| Reagents | Quantity | Reagents | Quantity |
| 96-well plate | 1 | Plate sealer for 96 wells | 4 |
| Pre-Mixed Standard | 2 | Standard Diluent | 1×20mL |
| Pre-Mixed Magnetic beads (22#:PDL1) | 1 | Analysis buffer | 1×20mL |
| Pre-Mixed Detection Reagent A | 1×120μL | Assay Diluent A | 1×12mL |
| Detection Reagent B (PE-SA) | 1×120μL | Assay Diluent B | 1×12mL |
| Sheath Fluid | 1×10mL | Wash Buffer (30 × concentrate) | 1×20mL |
| Instruction manual | 1 |
Assay procedure summary
1. Preparation of standards, reagents and samples before the experiment;
2. Add 100μL standard or sample to each well,
add 10μL magnetic beads, and incubate 90min at 37°C on shaker;
3. Remove liquid on magnetic frame, add 100μL prepared Detection Reagent A. Incubate 60min at 37°C on shaker;
4. Wash plate on magnetic frame for three times;
5. Add 100μL prepared Detection Reagent B, and incubate 30 min at 37°C on shaker;
6. Wash plate on magnetic frame for three times;
7. Add 100μL sheath solution, swirl for 2 minutes, read on the machine.
GIVEAWAYS
INCREMENT SERVICES
| Magazine | Citations |
| Chinese Journal of Cancer | Level of circulating PD-L1 expression in patients with advanced gastric cancer and its clinical implications NCBI: PMC3937742 |
| Leukemia.? | High level of soluble programmed cell death ligand 1 in blood impacts overall survival in aggressive diffuse large B-Cell lymphoma: results from a French multicenter clinical trial. Pubmed:24732592 |
| Diabetes?Metab Res Rev. | PD‐L1 gene polymorphisms and low serum level of PD‐L1 protein are associated to type 1 diabetes in Chile Pubmed:24816853 |
| Lancet Haematol | Ratios of T-cell immune effectors and checkpoint molecules as prognostic biomarkers in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a population-based study PubMed: 26686046 |
| Eur J Cancer. | High levels of the soluble programmed death-ligand (sPD-L1) identify hepatocellular carcinoma patients with a poor prognosis. Pubmed:27039170 |
| Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology | Serum levels of soluble programmed cell death ligand 1 as a prognostic factor on the first-line treatment of metastatic or recurrent gastric cancer article:10.1007 |
| Journal of Hematology & Oncology | PD-L1 is upregulated by EBV-driven LMP1 through NF-κB pathway and correlates with poor prognosis in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma pubmed:27737703 |
| Lung Cancer. | High plasma levels of soluble programmed cell death ligand 1 are prognostic for reduced survival in advanced lung cancer. pubmed:28212990 |
| Oncotarget | Soluble programmed death-ligand 1 (sPDL1) and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) predictssurvival in advanced biliary tract cancer patients treated with palliative chemotherapy. pubmed:27780932 |
| Oncotarget | High post-treatment serum levels of soluble programmed cell death ligand 1 predict earlyrelapse and poor prognosis in extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma patients. pubmed:27105512 |
| Oncotarget. | Soluble PD-L1: A biomarker to predict progression of autologous transplantation in patients with multiple myeloma pubmed:27566569 |
| Cancer Immunol Immunother. | Programmed death-ligand 1 and its soluble form are highly expressed in nasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma: a potential rationale for immunotherapy. pubmed:28349165 |
| Leukemia | Soluble programmed death-ligand 1 as a prognostic biomarker for overall survival in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a replication study and combined analysis of 508 patients leu2016385a |
| Medicine | Plasma levels of soluble programmed death ligand-1 may be associated with overall survival in nonsmall cell lung cancer patients receiving thoracic radiotherapy. pubmed:28207525 |
| Allergology International | Inverse correlation of soluble programmed cell death-1 ligand-1 (sPD-L1) with eosinophil count and clinical severity in allergic rhinitis patients pubmed:27617656 |
| Medicine | Plasma levels of soluble programmed death ligand-1 may be associated with overall survival in nonsmall cell lung cancer patients receiving thoracic radiotherapy PMC5319514 |
| American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine | Soluble Programed Death Receptor 1 Ligand (sPD-L1) in Pleural Fluid of Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma (MPM) Pdf:10.1164 |
| Clinical Lung Cancer | Soluble Programmed Cell Death Ligand 1 as a Novel Biomarker for Nivolumab Therapy for Non–Small-cell Lung Cancer Pubmed:29859759 |
| Journal of Rheumatology | Increased levels of soluble programmed death ligand 1 associate with malignancy in patients with dermatomyositis Pubmed:29419471 |
| Translational Oncology | High Serum Level of Soluble Programmed Death Ligand 1 is Associated With a Poor Prognosis in Hodgkin Lymphoma Pubmed:29698935 |
| Immunology Letters | Increased levels of soluble co-stimulatory molecule PD-L1 (B7-H1) in the plasma of viraemic HIV-1+ individuals Pubmed: 30236481 |
| Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology | Pre-treatment serum levels of soluble programmed cell death-ligand 1 predict prognosis in patients with hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma Pubmed: 30267213 |
| Annals of Surgical Oncology | Soluble PD-L1 Expression in Circulation as a Predictive Marker for Recurrence and Prognosis in Gastric Cancer: Direct Comparison of the Clinical Burden Between … Pubmed: 30565045 |
| American Journal of Reproductive Immunology | Identification of programmed cell death 1 and its ligand in the testicular tissue of mice Pubmed: 30578744 |
| PLoS One | Clinical significance of soluble programmed cell death-1 and soluble programmed cell death-ligand 1 in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer treated … Pubmed: 30807610 |
| Endocrine Connections | Elevated levels of soluble PD-L1 are associated with reduced recurrence in papillary thyroid cancer Pubmed: 31252406 |
| Scientific Reports | Prognostic implications of soluble programmed death-ligand 1 and its dynamics during chemotherapy in unresectable pancreatic cancer Pubmed: 31366979 |
| Critical Reviews in Oncology / Hematology | The Clinical Significance of Soluble PD-1 and PD-L1 in Lung Cancer Pubmed: 31675543 |
| PLoS One | Clinical implications of APOBEC3A and 3B expression in patients with breast cancer Pubmed: 32176735 |
| Cancers | Predictive Value of Soluble PD-1, PD-L1, VEGFA, CD40 Ligand and CD44 for Nivolumab Therapy in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Case-Control Study Pubmed: 32085544 |
| Serum levels of soluble programmed death-ligand 1 (sPD-L1) in patients with primary central nervous system diffuse large B-cell lymphoma Pubmed: 32054467 | |
| LIVER INTERNATIONAL | The prognostic role of soluble transforming growth factor‐β and its correlation with soluble programmed death‐ligand 1 in biliary tract cancer Pubmed: 32780918 |
| CANCER IMMUNOLOGY IMMUNOTHERAPY | Prognostic impacts of tumoral expression and serum levels of PD-L1 and CTLA-4 in colorectal cancer patients Pubmed: 32577816 |
| Soluble PD-L1: a potential immune marker for HIV-1 infection and virological failure Pubmed: 32443313 | |
| Cancer Immunol Immunother | The clinical implication of soluble PD-L1 (sPD-L1) in patients with breast cancer and its biological function in regulating the function of T lymphocyte 33688997 |
| Acta Biochim Biophys Sin | Prognostic prospect of soluble programmed cell death ligand-1 (sPD-L1) in cancer management 34180502 |
| EMBO J | Microglial PD‐1 stimulation by astrocytic PD‐L1 suppresses neuroinflammation and Alzheimer's disease pathology 34825707 |
| Mol Pharm | A Novel Small Cyclic Peptide-Based 68Ga-Radiotracer for Positron Emission Tomography Imaging of PD-L1 Expression in Tumors 34910492 |
| Mol Hum Reprod | Macrophage Associated Immune Checkpoint CD47 Blocking Ameliorates Endometriosis Pubmed:35404426 |
| Journal of Nanobiotechnology | Microbial hydrogen “manufactory” for enhanced gas therapy and self-activated immunotherapy via reduced immune escape Pubmed:35705974 |
| Medicina | Assessment of the RANTES Level Correlation and Selected Inflammatory and Pro-Angiogenic Molecules Evaluation of Their Influence on CRC Clinical Features: A … Pubmed:35208526 |