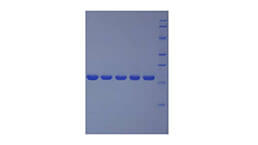
Active S100 Calcium Binding Protein (S100)
S100-A1; S100A1; S100-Alpha; S-100 Protein; S-100 protein subunit alpha; S-100 protein alpha chain
- Product No.APA012Hu01
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
- Buffer FormulationPBS, pH7.4, containing 0.01% SKL, 5% Trehalose.
- Traits Freeze-dried powder
- Purity> 97%
- Isoelectric Point4.8
- ApplicationsCell culture; Activity Assays.
- DownloadInstruction Manual
- UOM 10µg50µg 200µg 1mg 5mg
- FOB
US$ 160
US$ 400
US$ 800
US$ 2400
US$ 6000
For more details, please contact local distributors!
ACTIVITY TEST
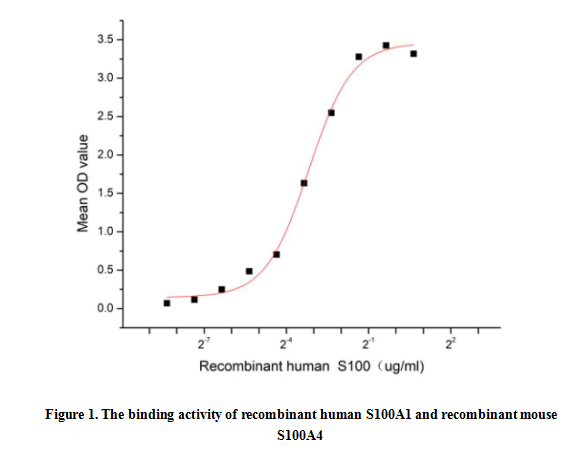
Small calcium binding protein that S100 Calcium Binding Protein (S100), also known as S100 Alpha (S100A1), is a member of the S100 family of calcium-binding proteins. As with most S100 proteins, S100A1 proteins are localized in the cytoplasm and/or nucleus of a wide range of cells, and it possess a variety of intracellular and extracellular functions. They interact with multiple receptors and signal transducers to regulate pathways that govern inflammation, cell differentiation, proliferation, energy metabolism, apoptosis, calcium homeostasis, cell cytoskeleton and microbial resistance. S100 Calcium Binding Protein A4 (S100A4) is one of targets of S100A1. Thus a functional binding ELISA assay was conducted to detect the interaction of recombinant human S100A1 and recombinant mouse S100A4. Briefly, S100A1 was diluted serially in PBS with 0.01% BSA (pH 7.4). Duplicate samples of 100 μl were then transferred to S100A4-coated microtiter wells and incubated for 1h at 37℃. Wells were washed with PBST and incubated for 1h with anti-S100A1 pAb, then aspirated and washed 3 times. After incubation with HRP labelled secondary antibody for 1h at 37℃, wells were aspirated and washed 5 times. With the addition of substrate solution, wells were incubated 15-25 minutes at 37℃. Finally, add 50 µL stop solution to the wells and read at 450/630 nm immediately. The binding activity of recombinant human S100A1 and recombinant mouse S100A4 was shown in Figure 1, the EC50 for this effect is 0.11 ug/mL.
USAGE
Reconstitute in 10mM PBS (pH7.4) to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL. Do not vortex.
STORAGE
Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8°C for one month. Aliquot and store at -80°C for 12 months.
STABILITY
The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37°C for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
GIVEAWAYS
INCREMENT SERVICES
-
 BCA Protein Quantification Kit
BCA Protein Quantification Kit
-
 Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
-
 Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
-
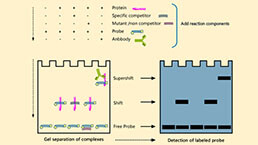 Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
-
 Buffer
Buffer
-
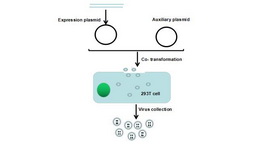 Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
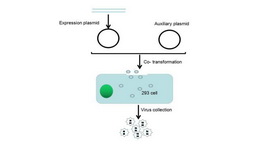 Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
-
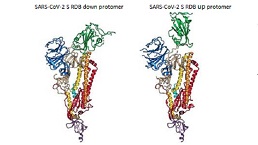 Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
-
 Protein G
Protein G
-
 Protein A
Protein A
| Magazine | Citations |
| Brain Research | Vasoactive intestinal peptide protects against ischemic brain damage induced by focal cerebral ischemia in rats ScienceDirect: S0006899311008663 |
| J Exp Neurosci | A New Technique for Collection of Cerebrospinal Fluid in Rat Pups PubMed: 26056488 |
| PLoS One | Regulation of Nutritional Metabolism in Transition Dairy Cows: Energy Homeostasis and Health in Response to Post-Ruminal Choline and Methionine pubmed:27501393 |
| brain research | Ellagic acid exerts protective effect in intrastriatal 6-hydroxydopamine rat model of Parkinson's disease: Possible involvement of ERβ/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling. pubmed:28238669 |
| КиберЛенинка | Levels of neurotropic autoantibodies in patients with schizophrenia article:n |
| Biomed Research International | Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Reduces Neuronal Apoptosis in Rats after Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion Injury via PI3K/AKT/eNOS Signaling Pathway Pubmed:29770336 |
| Metabolic Brain Disease | Trigonelline protects hippocampus against intracerebral Aβ (1–40) as a model of Alzheimer's disease in the rat: insights into underlying mechanisms Pubmed: 30421246 |
| ВОЗМОЖНОСТЬ ПРОГНОЗИРОВАНИЯ ОСТРОЙ НЕСПЕЦИФИЧЕСКОЙ БОЛИ В НИЖНЕЙ ЧАСТИ СПИНЫ С ИСПОЛЬЗОВАНИЕМ СЫВОРОТОЧНЫХ … | |
| ВЛИЯНИЕ ХРОНИЧЕСКОГО ВВЕДЕНИЯ НЕЙРОЛЕПТИКОВ НА УРОВНИ НЕЙРОСПЕЦИФИЧЕСКИХ АУТОАНТИТЕЛ В КРОВИ У КРЫС |