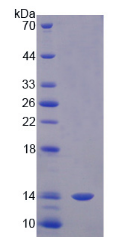
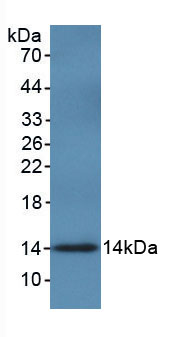
Active Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF)
GIF; GLIF; MMIF; Glycosylation-Inhibiting Factor; L-dopachrome isomerase; L-dopachrome tautomerase; Phenylpyruvate tautomerase
- Product No.APA698Hu01
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
- Buffer FormulationPBS, pH7.4, containing 0.05% SKL, 1mM DTT, 5% Trehalose and Proclin300.
- Traits Freeze-dried powder
- Purity> 90%
- Isoelectric Point7.1
- ApplicationsCell culture; Activity Assays.
- DownloadInstruction Manual
- UOM 10µg50µg 200µg 1mg 5mg
- FOB
US$ 322
US$ 806
US$ 1612
US$ 4836
US$ 12090
For more details, please contact local distributors!
ACTIVITY TEST

Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF), also known as glycosylation- inhibiting factor (GIF), L-dopachrome isomerase, or phenylpyruvate tautomerase is a protein classified as an inflammatory cytokine. MIF is an important regulator of innate immunity. It involved in cell-mediated immunity, immunoregulation, and inflammation. MIF plays a role in the regulation of macrophage function in host defense through the suppression of anti-inflammatory effects of glucocorticoids. This lymphokine and the JAB1 protein form a complex in the cytosol near the peripheral plasma membrane, which may indicate a role in integrin signaling pathways. Besides, Major Histocompatibility Complex Class II Invariant Chain (MHCDG) has been identified as an interactor of MIF, thus a binding ELISA assay was conducted to detect the interaction of recombinant human MIF and recombinant human MHCDG. Briefly, MIF were diluted serially in PBS, with 0.01% BSA (pH 7.4). Duplicate samples of 100uL were then transferred to MHCDG- coated microtiter wells and incubated for 2h at 37℃. Wells were washed with PBST and incubated for 1h with anti-MIF pAb, then aspirated and washed 3 times. After incubation with HRP labelled secondary antibody, wells were aspirated and washed 3 times. With the addition of substrate solution, wells were incubated 15-25 minutes at 37℃. Finally, add 50µL stop solution to the wells and read at 450nm immediately. The binding activity of MIF and MHCDG was shown in Figure 1, and this effect was in a dose dependent manner.
Figure. The binding activity of MIF with MHCDG.

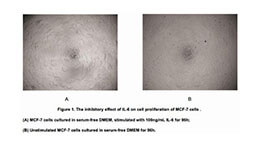
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF or MMIF), is a lymphokine involved in cell-mediated immunity, immunoregulation, and inflammation. MIF contains two motifs with catalytic activity. The first is a 27 amino acid motif located at the N-terminus functions as a phenylpyruvate tautomerase. MIF also contains a Cys-Ala-Leu-Cys catalytic site between residues 57 and 60 that appears to function as a disulfide reductase. Besides, MIF is overexpressed in various tumors and has been suggested as a molecular link between chronic inflammation and cancer. To measured the effect of MIF on cell proliferation, breast cancer MCF-7 cells were seeded into triplicate wells of 96-well plates at a density of 5,000 cells/well and allowed to attach, replaced with serum-free overnight, then the medium was replaced with 1% serum standard DMEM prior to the addition of various concentrations of recombinant human MIF. After incubated for 96h, cells were observed by inverted microscope and cell proliferation was measured by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8). Briefly, 10µL of CCK-8 solution was added to each well of the plate, then the absorbance at 450nm was measured using a microplate reader after incubating the plate for 1-4 hours at 37℃. Proliferation of MCF-7 cells after incubation with MIF for 96h observed by inverted microscope was shown in Figure 2. Cell viability was assessed by CCK-8 assay after incubation with recombinant MIF for 96h. The result was shown in Figure 3. It was obvious that MIF significantly increased cell viability of MCF-7 cells.
(A) MCF-7 cells cultured in DMEM, stimulated with 10ng/mL MIF for 96h;
(B) Unstimulated MCF7 cells cultured in DMEM for 96h.
Figure. Cell proliferation of MCF-7 cells after stimulated with MIF.

Figure. Cell proliferation of MCF-7 cells after stimulated with MIF.
USAGE
Reconstitute in 10mM PBS (pH7.4) to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL. Do not vortex.
STORAGE
Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8°C for one month. Aliquot and store at -80°C for 12 months.
STABILITY
The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37°C for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
GIVEAWAYS
INCREMENT SERVICES
-
 BCA Protein Quantification Kit
BCA Protein Quantification Kit
-
 Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
-
 Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
-
 Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
-
 Buffer
Buffer
-
 Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
 Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
-
 Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
-
 Protein G
Protein G
-
 Protein A
Protein A
| Magazine | Citations |
| Kidney International | Targeted reduction of advanced glycation improves renal function in obesity PubMed: 21412218 |
| The Journal of Immunology | Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor Plays a Role in the Regulation of Microfold (M) Cell-Mediated Transport in the Gut Jimmunol: 5673 |
| The Journal of Endocrinology | Involvement of exercise-induced macrophage migration inhibitory factor in the prevention of fatty liver disease PubMed: PMC3757527 |
| The Journal of Immunology | Role of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in the regulatory T cell response of tumor-bearing mice PubMed: PMC3466372 |
| Diabetologia | Deletion of bone-marrow-derived receptor for AGEs (RAGE) improves renal function in an experimental mouse model of diabetes Pubmed:24957662 |
| BioMed Research International | The Potential Role of Polymethyl Methacrylate as a New Packaging Material for the Implantable Medical Device in the Bladder PubMed: 25705692 |
| Diabetologia | Combined NOX1/4 inhibition with GKT137831 in mice provides dose-dependent reno- and atheroprotection even in established micro- and macrovascular disease. pubmed:28160092 |
| Life Sciences | Protective effect of chlorogenic acid on the inflammatory damage of pancreas and lung in mice with l-arginine-induced pancreatitis pubmed:28919396 |
| Scientific Reports | Cytokine MIF Enhances Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability: Impact for Therapy in Ischemic Stroke Pubmed:29335619 |
| Ocular Immunology and Inflammation | Immune Response and Mechanisms of IFN-γ in Administration for Keratomycosis Pubmed: 30307777 |
| International Journal of Immunopathology and Pharmacology | Effect of voluntary running on expression of myokines in brains of rats with depression Pubmed: 30834799 |
| Biomarkers in Heart Failure and Associated Diseases | Biomarkers in Heart Failure and Associated Diseases |
| Science China-Life Sciences | Autophagy mediates the secretion of macrophage migration inhibitory factor from cardiomyocytes upon serum-starvation Pubmed: 31209799 |
| Folia Morphologica | Beneficial effects of voluntary over forced exercise on skeletal muscle structure and myokines expression Pubmed: 31802473 |
| Biomed Pharmacother | Deletion of macrophage migration inhibitory factor ameliorates inflammation in mice model severe acute pancreatitis Pubmed: 32062385 |
| Sci Rep | Association between MIF gene promoter rs755622 and susceptibility to coronary artery disease and inflammatory cytokines in the Chinese Han population 33850223 |
| Commun Biol | Macrophage migration inhibitory factor is overproduced through EGR1 in TET2low resting monocytes Pubmed:35115654 |