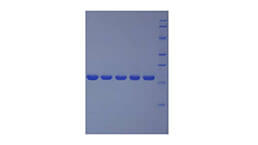
Active Apolipoprotein A1 (APOA1)
Apo-A1; ApoA-1 Milano; ProapoA-I; Proapolipoprotein A-I; Truncated apolipoprotein A-I
- Product No.APA519Po01
- Organism SpeciesSus scrofa; Porcine (Pig) Same name, Different species.
- Buffer FormulationPBS, pH7.4, containing 0.01% SKL, 5% Trehalose.
- Traits Freeze-dried powder
- Purity> 95%
- Isoelectric Point4.9
- ApplicationsCell culture; Activity Assays.
- DownloadInstruction Manual
- UOM 10µg50µg 200µg 1mg 5mg
- FOB
US$ 264
US$ 660
US$ 1320
US$ 3960
US$ 9900
For more details, please contact local distributors!
ACTIVITY TEST
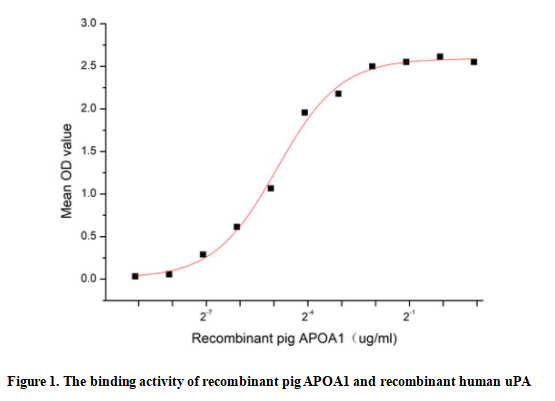
Apolipoprotein A1 (APOA1) is the major protein component of HDL particles in plasma. It is a cofactor for lecithin cholesterolacyltransferase (LCAT) which is responsible for the formation of most plasma cholesteryl esters. ApoA1 was also isolated as a prostacyclin (PGI2) stabilizing factor, and thus may have an anticlotting effect. ApoA1 is often used as a biomarker for prediction of cardiovascular diseases. Besides, Plasminogen Activator, Urokinase (uPA) has been identified as an interactor of APOA1, thus a functional binding ELISA assay was conducted to detect the interaction of recombinant pig APOA1 and recombinant human uPA. Briefly, APOA1 were diluted serially in PBS, with 0.01% BSA (pH 7.4). Duplicate samples of 100 ul were then transferred to uPA-coated microtiter wells and incubated for 2h at 37℃. Wells were washed with PBST and incubated for 1h with anti-APOA1 pAb, then aspirated and washed 3 times. After incubation with HRP labelled secondary antibody, wells were aspirated and washed 3 times. With the addition of substrate solution , wells were incubated 15-25 minutes at 37℃. Finally, add 50 µL stop solution to the wells and read at 450/630 nm immediately. The binding activity of recombinant pig APOA1 and recombinant human uPA was shown in Figure 1, the EC50 for this effect was 0.03 ug/mL.
USAGE
Reconstitute in 10mM PBS (pH7.4) to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL. Do not vortex.
STORAGE
Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8°C for one month. Aliquot and store at -80°C for 12 months.
STABILITY
The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37°C for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
GIVEAWAYS
INCREMENT SERVICES
-
 BCA Protein Quantification Kit
BCA Protein Quantification Kit
-
 Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
-
 Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
-
 Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
-
 Buffer
Buffer
-
 Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
 Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
-
 Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
-
 Protein G
Protein G
-
 Protein A
Protein A
| Magazine | Citations |
| European Journal of Applied Physiology | Endurance training enhances ABCA1 expression in rat small intestine PubMed: 19629515 |
| Official Journal of the INWR | Effect of eight weeks of wrestling and circuit fitness training on Apo lipoportein A-I and lymphocyte ABCA1 gene expression in well-trained wrestler. Wrestling: source |
| Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications | Treadmill exercise enhances ABCA1 expression in rat liver ScienceDirect: S0006291X0701488X |
| World Journal of Sport Sciences | The Effect of Eight Weeks of Wrestling and Wrestling Technique Based Circuit Training on Lymphocyte ABCA1 Gene Expression and Plasma Apolipoprotein A-1 Idosi: source |
| Biochimica et Biophysica Acta | Hepatic lipase- and endothelial lipase-deficiency in mice promotes macrophage-to-feces RCT and HDL antioxidant properties PubMed: 23328279 |
| Biomarkers | The association of a distinct plasma proteomic profile with the cervical high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion of Uyghur women: a 2D liquid-phase chromatography/mass spectrometry study PubMed: 22458349 |
| Journal of the American Heart Association | MicroRNA-33 Deficiency Reduces the Progression of Atherosclerotic Plaque in ApoE?/? Mice PubMed: PMC3540673 |
| PLoS ONE | Apolipoprotein AI Is a Potential Mediator of Remote Ischemic Preconditioning Plosone: Source |
| Molecular Genetics and Metabolism | DYRK1A overexpression decreases plasma lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase activity and apolipoprotein AI levels Pubmed: 23920041 |
| Endocrinology | Deficiency of Clusterin Exacerbates High-Fat Diet-Induced Insulin Resistance in Male Mice Pubmed: 24684302 |
| Molecular Genetics and Metabolism Reports | Corrective effects of hepatotoxicity by hepatic Dyrk1a gene delivery in mice with intermediate hyperhomocysteinemia Sciencedirect:S2214426915000026 |
| J Psychopharmacol | Anti-atherogenic properties of high-density lipoproteins in psychiatric patients before and after two months of atypical anti-psychotic therapy PubMed: 26253619 |
| Biochim Biophys Acta | Culturing of HepG2 cells with human serum improve their functionality and suitability in studies of lipid metabolism PubMed: 26515253 |
| Pharmacol Res Perspect | Efficacy of tomato concentrates in mouse models of dyslipidemia and cancer PubMed: 26171234 |
| Clin Exp Nephrol | Differentially expressed urinary biomarkers in children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome PubMed: 26351173 |
| Oncogene | Apolipoprotein A-I inhibits experimental colitis and colitis-propelled carcinogenesis PubMed: 26279300 |
| Oncogene | Apolipoprotein AI inhibits experimental colitis and colitis-propelled carcinogenesis Pubmed:26279300 |
| Allergy | Serum levels of 9α,11β-PGF2 and apolipoprotein A1 achieve high predictive power as biomarkers of anaphylaxis. pubmed:28378321 |
| Journal of Chromatography A | Application of a new procedure for liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry profiling of plasma amino acid-related metabolites and untargeted shotgun proteomics to identify mechanisms and biomarkers of calcific aortic stenosis S0021967317311858 |
| 11 | High-Density Lipoproteins Exert Pro-inflammatory Effects on Macrophages via Passive Cholesterol Depletion and PKC-NF-kB/STAT1-IRF1 Signaling pubmed:27866837 |
| Biomedical Science Letters | Effect of Ginkgo biloba Extract (EGb 761) on Serum Cholesterol Levels in Wild-type C57Bl/6 Mice 10.15616/BSL.2017.23.2.80 |
| ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering | Enhanced Antiatherosclerotic Efficacy of Statin-Loaded Reconstituted High-Density Lipoprotein via Ganglioside GM1 Modification abs:10.1021 |
| Food Research International | Wild Lonicera caerulea berry polyphenol extract reduces cholesterol accumulation and enhances antioxidant capacity in vitro and in vivo Pubmed:29580541 |
| Journal of The Science of Food and Agriculture | Consumption of orange fermented beverage improves antioxidant status and reduces peroxidation lipid and inflammatory markers in healthy humans Pubmed:29124773 |
| Toxicon | A membrane disrupting toxin from wasp venom underlies the molecular mechanism of tissue damage Pubmed:29654869 |
| European Journal of Pharmacology | The effect of exenatide (a GLP-1 analog) and sitagliptin (a DPP-4 inhibitor) on plasma platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase (PAF-AH) activity and concentration in?… Pubmed: 30768981 |
| European Journal of Preventive Cardiology | High-intensity interval training has a greater effect on reverse cholesterol transport elements compared with moderate-intensity continuous training in obese male rats Pubmed: 31718266 |
| Diagnostics | Systemic Alterations of Immune Response-Related Proteins during Glaucoma Development in the Murine Model DBA/2J Pubmed: 32585848 |
| VETERINARY PATHOLOGY | Pathology and Proteomics-Based Diagnosis of Localized Light-Chain Amyloidosis in Dogs and Cats Pubmed: 32880234 |
| Nat Commun | GP73 is a TBC-domain Rab GTPase-activating protein contributing to the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease without obesity 34853313 |
| Cardiovasc Toxicol | Interplay of Obesity, Ethanol, and Contaminant Mixture on Clinical Profiles of Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases: Evidence from an Animal Study Pubmed:35429258 |
| Peptides | Neuropeptide Y promotes hepatic apolipoprotein A1 synthesis and secretion through neuropeptide Y Y5 receptor Pubmed:35660638 |
| Journal of Functional Foods | Castanea mollissima shell polyphenols regulate JAK2 and PPARγ expression to suppress inflammation and lipid accumulation by inhibiting M1 macrophages … |