Packages (Simulation)

Reagent Preparation
Image (I)
Image (II)
Certificate


ELISA Kit for Selenoprotein P1, Plasma (SEPP1)
SEPP; SeP; SEP-P1; SELP
- Product No.SEB809Hu
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
- Sample Typeserum, plasma and other biological fluids
- Test MethodDouble-antibody Sandwich
- Assay Length3h
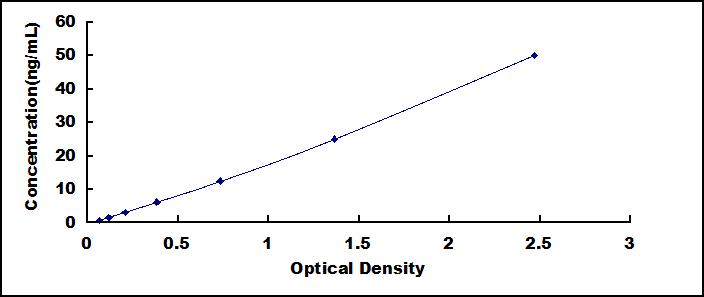
- Detection Range0.78-50ng/mL
- SensitivityThe minimum detectable dose of this kit is typically less than 0.31ng/mL.
- DownloadInstruction Manual
- UOM 48T96T 96T*5 96T*10 96T*100
- FOB
US$ 466
US$ 665
US$ 2993
US$ 5653
US$ 46550
For more details, please contact local distributors!
Specificity
This assay has high sensitivity and excellent specificity for detection of Selenoprotein P1, Plasma (SEPP1).
No significant cross-reactivity or interference between Selenoprotein P1, Plasma (SEPP1) and analogues was observed.
Recovery
Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of recombinant Selenoprotein P1, Plasma (SEPP1) and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of Selenoprotein P1, Plasma (SEPP1) in samples.
| Matrix | Recovery range (%) | Average(%) |
| serum(n=5) | 86-102 | 94 |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 82-101 | 87 |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 90-105 | 95 |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Selenoprotein P1, Plasma (SEPP1) were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Selenoprotein P1, Plasma (SEPP1) were tested on 3 different plates, 8 replicates in each plate.
CV(%) = SD/meanX100
Intra-Assay: CV<10%
Inter-Assay: CV<12%
Linearity
The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of Selenoprotein P1, Plasma (SEPP1) and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| Sample | 1:2 | 1:4 | 1:8 | 1:16 |
| serum(n=5) | 88-95% | 89-103% | 97-105% | 92-99% |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 80-90% | 92-102% | 82-104% | 81-96% |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 79-93% | 94-102% | 84-93% | 86-102% |
Stability
The stability of kit is determined by the loss rate of activity. The loss rate of this kit is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
To minimize extra influence on the performance, operation procedures and lab conditions, especially room temperature, air humidity, incubator temperature should be strictly controlled. It is also strongly suggested that the whole assay is performed by the same operator from the beginning to the end.
Reagents and materials provided
| Reagents | Quantity | Reagents | Quantity |
| Pre-coated, ready to use 96-well strip plate | 1 | Plate sealer for 96 wells | 4 |
| Standard | 2 | Standard Diluent | 1×20mL |
| Detection Reagent A | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent A | 1×12mL |
| Detection Reagent B | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent B | 1×12mL |
| TMB Substrate | 1×9mL | Stop Solution | 1×6mL |
| Wash Buffer (30 × concentrate) | 1×20mL | Instruction manual | 1 |
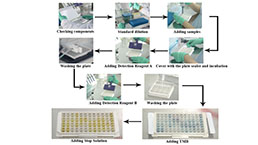
Assay procedure summary
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards;
2. Add 100µL standard or sample to each well. Incubate 1 hours at 37°C;
3. Aspirate and add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent A. Incubate 1 hour at 37°C;
4. Aspirate and wash 3 times;
5. Add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent B. Incubate 30 minutes at 37°C;
6. Aspirate and wash 5 times;
7. Add 90µL Substrate Solution. Incubate 10-20 minutes at 37°C;
8. Add 50µL Stop Solution. Read at 450nm immediately.
GIVEAWAYS
INCREMENT SERVICES
-
 Single-component Reagents of Assay Kit
Single-component Reagents of Assay Kit
-
 Lysis Buffer Specific for ELISA / CLIA
Lysis Buffer Specific for ELISA / CLIA
-
 Quality Control of Kit
Quality Control of Kit
-
 ELISA Kit Customized Service
ELISA Kit Customized Service
-
 Disease Model Customized Service
Disease Model Customized Service
-
 Serums Customized Service
Serums Customized Service
-
 TGFB1 Activation Reagent
TGFB1 Activation Reagent
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
-
 Streptavidin
Streptavidin
-
 Fast blue Protein Stain solution
Fast blue Protein Stain solution -
 Single-component Reagents of FLIA Kit
Single-component Reagents of FLIA Kit
-
 Streptavidin-Agarose Beads
Streptavidin-Agarose Beads
| Magazine | Citations |
| The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism | Serum Selenoprotein P Levels in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Prediabetes: Implications for Insulin Resistance, Inflammation, and Atherosclerosis PubMed: 21677040 |
| Diabetes & metabolism journal | Increased Selenoprotein P Levels in Subjects with Visceral Obesity and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease PubMed: 23439771 |
| Journal of Pediatric Biochemistry | Trace elements, heavy metals and vitamins in Egyptian school children with iron deficiency anemia Metapress:Source |
| Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology | Selenium and its relationship with selenoprotein P and glutathione peroxidase in children and adolescents with Hashimoto's thyroiditis and hypothyroidism PubMed: 26854239 |
| OBES RES CLIN PRACT/OBESITY RESEARCH & CLINICAL PRACTICE | Selenoprotein P is elevated in individuals with obesity, but is not independently associated withinsulin resistance. pubmed:27524654 |
| Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism | Acute Overfeeding Does Not Alter Liver or Adipose Tissue-Derived Cytokines in HealthyHumans. pubmed:27832637 |
| European Journal of Nutrition | DNA damage and oxidative stress response to selenium yeast in the non-smoking individuals: ashort-term supplementation trial with respect to GPX1 and SEPP1 polymorphism. pubmed:26658762 |
| South. Clin. Ist. Euras. | Evaluation of the Relationship Between Insulin Resistance and Selenoprotein P in Patients with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome DOI: 10.14744/scie.2017.87597 |
| Arch Endocrinol Metab | Serum selenium and selenoprotein-P levels in autoimmune thyroid dieases patients in a select center a transversal study DOI: 10.1590/2359-3997000000309 |
| British Journal of Nutrition | Selenium, selenoproteins and selenometabolites in mothers and babies at the time of birth pubmed:28534447 |
| Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology | Biomarkers of selenium status and antioxidant effect in workers occupationally exposed to mercury Pubmed:29895371 |
| Biological & Pharmceutical Bulletin | Comparison of Human Selenoprotein P Determinants in Serum between Our Original Methods and Commercially Available Kits Pubmed:29709922 |
| Diabetologia | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in the first trimester and subsequent development of gestational diabetes mellitus Pubmed: 30470912 |
| Biological Trace Element Research | Selenium Levels in Community Dwellers with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Pubmed: 30725267 |
| Advances in Medical Sciences | Can hepatokines be regarded as novel non-invasive serum biomarkers of intrahepatic lipid content in obese children? Pubmed: 30921653 |
| Acute swimming exercise, but not exposure to moderate hypoxic conditions reduces circulating selenoprotein P levels in short-term, high-fat diet-fed rats Pubmed: 31236416 | |
| Hormones | Selenium and selenoprotein P in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease Pubmed: 31493247 |
| Bull Environ Contam Toxicol | Soil Selenium Concentration and Residents Daily Dietary Intake in a Selenosis Area: A Preliminary Study in Yutangba Village, Enshi City, China Pubmed: 32909074 |
| INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR SCIENCES | Higher Serum Selenoprotein P Level as a Novel Inductor of Metabolic Complications in Psoriasis Pubmed: 32605214 |
| Circulating hepassocin level in patients with stable angina is associated with fatty liver and renal function | |
| Nat Immunol | Selenium–GPX4 axis protects follicular helper T cells from ferroptosis 34413521 |
| Reviews in Cardiovascular Medicine | Selenoprotein P-1 (SEPP1) as An Early Biomarker of Acute Kidney Injury in Patients Undergoing Cardiopulmonary Bypass |