Packages (Simulation)

Reagent Preparation
Image (I)
Image (II)
Certificate


ELISA Kit for Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor Gamma (PPARg)
PPAR-G; PPARG1; PPARG2; NR1C3; Glitazone Receptor; Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 1 Group C Member 3
- Product No.SEA886Ra
- Organism SpeciesRattus norvegicus (Rat) Same name, Different species.
- Sample Typeserum, plasma, tissue homogenates, cell lysates, cell culture supernates and other biological fluids
- Test MethodDouble-antibody Sandwich
- Assay Length3h
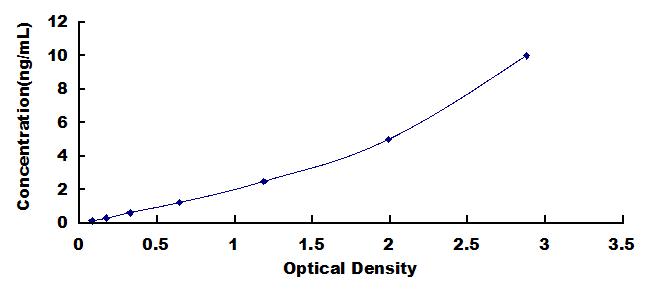
- Detection Range0.156-10ng/mL
- SensitivityThe minimum detectable dose of this kit is typically less than 0.057ng/mL.
- DownloadInstruction Manual
- UOM 48T96T 96T*5 96T*10 96T*100
- FOB
US$ 479
US$ 684
US$ 3078
US$ 5814
US$ 47880
For more details, please contact local distributors!
Specificity
This assay has high sensitivity and excellent specificity for detection of Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor Gamma (PPARg).
No significant cross-reactivity or interference between Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor Gamma (PPARg) and analogues was observed.
Recovery
Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of recombinant Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor Gamma (PPARg) and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor Gamma (PPARg) in samples.
| Matrix | Recovery range (%) | Average(%) |
| serum(n=5) | 90-102 | 96 |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 87-94 | 90 |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 90-103 | 94 |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor Gamma (PPARg) were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor Gamma (PPARg) were tested on 3 different plates, 8 replicates in each plate.
CV(%) = SD/meanX100
Intra-Assay: CV<10%
Inter-Assay: CV<12%
Linearity
The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor Gamma (PPARg) and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| Sample | 1:2 | 1:4 | 1:8 | 1:16 |
| serum(n=5) | 90-97% | 86-103% | 96-105% | 96-105% |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 85-92% | 88-103% | 85-97% | 98-105% |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 87-96% | 83-102% | 88-95% | 89-104% |
Stability
The stability of kit is determined by the loss rate of activity. The loss rate of this kit is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
To minimize extra influence on the performance, operation procedures and lab conditions, especially room temperature, air humidity, incubator temperature should be strictly controlled. It is also strongly suggested that the whole assay is performed by the same operator from the beginning to the end.
Reagents and materials provided
| Reagents | Quantity | Reagents | Quantity |
| Pre-coated, ready to use 96-well strip plate | 1 | Plate sealer for 96 wells | 4 |
| Standard | 2 | Standard Diluent | 1×20mL |
| Detection Reagent A | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent A | 1×12mL |
| Detection Reagent B | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent B | 1×12mL |
| TMB Substrate | 1×9mL | Stop Solution | 1×6mL |
| Wash Buffer (30 × concentrate) | 1×20mL | Instruction manual | 1 |
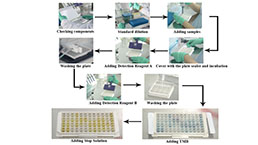
Assay procedure summary
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards;
2. Add 100µL standard or sample to each well. Incubate 1 hours at 37°C;
3. Aspirate and add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent A. Incubate 1 hour at 37°C;
4. Aspirate and wash 3 times;
5. Add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent B. Incubate 30 minutes at 37°C;
6. Aspirate and wash 5 times;
7. Add 90µL Substrate Solution. Incubate 10-20 minutes at 37°C;
8. Add 50µL Stop Solution. Read at 450nm immediately.
GIVEAWAYS
INCREMENT SERVICES
-
 Single-component Reagents of Assay Kit
Single-component Reagents of Assay Kit
-
 Lysis Buffer Specific for ELISA / CLIA
Lysis Buffer Specific for ELISA / CLIA
-
 Quality Control of Kit
Quality Control of Kit
-
 ELISA Kit Customized Service
ELISA Kit Customized Service
-
 Disease Model Customized Service
Disease Model Customized Service
-
 Serums Customized Service
Serums Customized Service
-
 TGFB1 Activation Reagent
TGFB1 Activation Reagent
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
-
 Streptavidin
Streptavidin
-
 Fast blue Protein Stain solution
Fast blue Protein Stain solution
-
 Single-component Reagents of FLIA Kit
Single-component Reagents of FLIA Kit
-
 Streptavidin-Agarose Beads
Streptavidin-Agarose Beads
| Magazine | Citations |
| Neuroscience Letters | Elevated levels of PPAR-gamma in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis Pubmed: 24021801 |
| J Cell Biochem. | Nonivamide enhances miRNA let‐7d expression and decreases adipogenesis PPARγ expression in 3T3‐L1 cells Pubmed:25704235 |
| Osteoarthritis Cartilage | Establishment of a rabbit model to study the influence of advanced glycation end products accumulation on osteoarthritis and the protective effect of pioglitazone PubMed: 26321377 |
| J Clin Diagn Res. | Evaluation of Protein Kinase Cβ and PPARγ Activity in Diabetic Rats Supplemented with Momordica charantia pmc:PMC4866090 |
| Journal of Clinical&Diagnostic Research | Evaluation of Protein Kinase Cβ and PPARγ Activity in Diabetic RatsSupplemented with Momordica charantia. pubmed:27190792 |
| Osteoarthritis and Cartilage | Establishment of a rabbit model to study the influence of advanced glycation end productsaccumulation on osteoarthritis and the protective effect of pioglitazone. pubmed:26321377 |
| Neuroscience Letters | Unlike PPARgamma, neither other PPARs nor PGC-1alpha is elevated in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis pubmed:28483651 |
| European Journal of Immunology | Engulfment of Hb‐activated platelets differentiates monocytes into pro‐inflammatory macrophages in PNH patients Pubmed:29677388 |
| Histochemistry and Cell Biology | Simpson–Golabi–Behmel syndrome human adipocytes reveal a changing phenotype throughout differentiation Pubmed:29574488 |
| molecular and cellular biochemistry | Maternal omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin E improve placental angiogenesis in late-onset but not early-onset preeclampsia Pubmed: 31420792 |
| Nutrients. | Hyperglycemia Changes Expression of Key Adipogenesis Markers (C/EBPα and PPARᵞ) and Morphology of Differentiating Human Visceral Adipocytes Pubmed: 31398873 |
| journal of biochemical and molecular toxicology | Indomethacin and juglone inhibit inflammatory molecules to induce apoptosis in colon cancer cells Pubmed: 31916655 |
| J Cosmet Dermatol | In©\vitro effect of pine bark extract on melanin synthesis, tyrosinase activity, production of endothelin©\1 and PPAR in cultured melanocytes exposed to Ultraviolet?¡ 33960120 |
| American Chemical Society | TRPA1 Agonist Cinnamaldehyde Decreases Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Cells More Potently than the Non-agonist Structural Analog Cinnamyl Isobutyrate 33403292 |
| PLoS One | Quantitative real-time measurement of endothelin-1-induced contraction in single non-activated hepatic stellate cells 34343209 |
| Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids | Maternal Vitamin D Deficiency Reduces Docosahexaenoic Acid, Placental Growth Factor and Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor Gamma levels in the Pup … 34768025 |
| Food and Chemical Toxicology | Melatonin attenuates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury in mice: Involvement of PPARα and fatty acid oxidation Pubmed:35367536 |