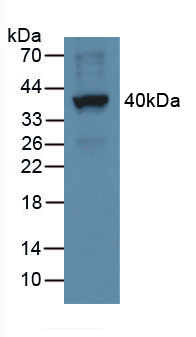
Polyclonal Antibody to Epithelial Neutrophil Activating Peptide 78 (ENA78)
CXCL5; SCYB5; Chemokine C-X-C-Motif Ligand 5; Small Inducible Cytokine Subfamily B(Cys-X-Cys),Member 5; Neutrophil-activating peptide ENA-78
- Product No.PAA860Hu03
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
- SourcePolyclonal antibody preparation
- HostRabbit
- Potencyn/a
- Ig Type IgG
- PurificationAntigen-specific affinity chromatography followed by Protein A affinity chromatography
- LabelNone
- Immunogen RPA860Hu03-Recombinant Epithelial Neutrophil Activating Peptide 78 (ENA78)
- Buffer FormulationPBS, pH7.4, containing 0.02% NaN3, 50% glycerol.
- TraitsLiquid
- Concentration0.5mg/mL
- Organism Species MoreMus musculus (Mouse)
- ApplicationsWB; IHC
If the antibody is used in flow cytometry, please check FCM antibodies. - DownloadInstruction Manual
- UOM 20µl100µl 200µl 1ml 10ml
- FOB
US$ 67
US$ 157
US$ 224
US$ 560
US$ 2240
For more details, please contact local distributors!
SPECIFITY
The antibody is a rabbit polyclonal antibody raised against ENA78. It has been selected for its ability to recognize ENA78 in immunohistochemical staining and western blotting.
USAGE
Western blotting: 0.01-5µg/mL;
Immunohistochemistry: 5-50µg/mL;
Immunocytochemistry: 5-50µg/mL;
Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
STORAGE
Store at 4°C for frequent use. Stored at -20°C in a manual defrost freezer for two year without detectable loss of activity. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
STABILITY
The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37°C for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
GIVEAWAYS
INCREMENT SERVICES
-
 Antibody Labeling Customized Service
Antibody Labeling Customized Service
-
 Protein A/G Purification Column
Protein A/G Purification Column
-
 Staining Solution for Cells and Tissue
Staining Solution for Cells and Tissue
-
 Positive Control for Antibody
Positive Control for Antibody
-
 Tissue/Sections Customized Service
Tissue/Sections Customized Service
-
 Phosphorylated Antibody Customized Service
Phosphorylated Antibody Customized Service
-
 Western Blot (WB) Experiment Service
Western Blot (WB) Experiment Service
-
 Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Experiment Service
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Experiment Service
-
 Immunocytochemistry (ICC) Experiment Service
Immunocytochemistry (ICC) Experiment Service
-
 Flow Cytometry (FCM) Experiment Service
Flow Cytometry (FCM) Experiment Service
-
 Immunoprecipitation (IP) Experiment Service
Immunoprecipitation (IP) Experiment Service
-
 Immunofluorescence (IF) Experiment Service
Immunofluorescence (IF) Experiment Service
-
 Buffer
Buffer
-
 DAB Chromogen Kit
DAB Chromogen Kit
-
 SABC Kit
SABC Kit
-
 Long-arm Biotin Labeling Kit
Long-arm Biotin Labeling Kit
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
| Magazine | Citations |
| Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology | Ameliorative Effects of Curcumin on Fibrinogen-Like Protein-2 Gene Expression, Some Oxido-Inflammatory and Apoptotic Markers in a Rat Model of l-Arginine-Induced Acute Pancreatitis. Pubmed:26862043 |
| Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology | Ameliorative Effects of Curcumin on Fibrinogen-Like Protein-2 Gene Expression, Some Oxido-Inflammatory and Apoptotic Markers in a Rat Model of l-Arginine-Induced Acute Pancreatitis pubmed:26862043 |
| OncoTargets and Therapy | The clinical significance of CXCL5 in non-small cell lung cancer. pubmed:29200871 |
| Biochimie | Activated CXCL5-CXCR2 axis promotes the migration, invasion and EMT of papillary thyroid carcinoma cells via modulation of β-catenin pathway Pubmed:29471001 |
| Cancer Biology & Therapy | Activation of CXCL5-CXCR2 axis promotes proliferation and accelerates G1 to S phase transition of papillary thyroid carcinoma cells and activates JNK and p38 … Pubmed: 30404567 |
| Respiratory Research | Phospholipase Cε plays a crucial role in neutrophilic inflammation accompanying acute lung injury through augmentation of CXC chemokine production from … Pubmed: 30634975 |
| American Journal of Pathology | Interleukin17–CXCR2 axis facilitates breast cancer progression by up-regulating neutrophil recruitment Pubmed: 31654638 |
| Bioactive Materials | Secretions from hypochlorous acid-treated tumor cells delivered in a melittin hydrogel potentiate cancer immunotherapy 34820587 |
| Am J Cancer Res | Differential expression profile of CXC-receptor-2 ligands as potential biomarkers in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma Pubmed:35141005 |