Packages (Simulation)

Reagent Preparation
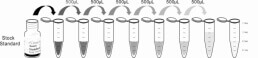
Image (I)
Image (II)
Certificate


High Sensitive ELISA Kit for Activated Protein C (APC)
- Product No.HEA738Hu
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
- Sample Typeplasma
- Test MethodDouble-antibody Sandwich
- Assay Length3h
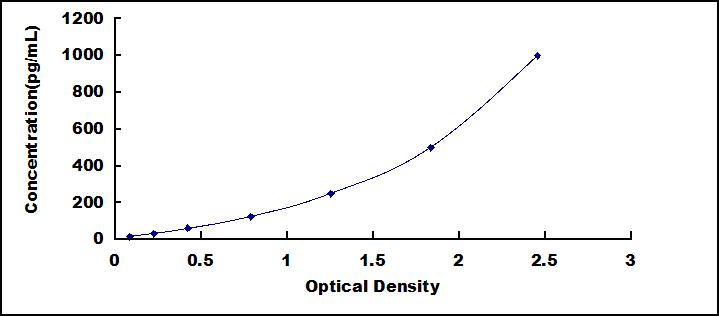
- Detection Range15.6-1,000pg/mL
- SensitivityThe minimum detectable dose of this kit is typically less than 6.1pg/mL.
- DownloadInstruction Manual
- UOM 48T96T 96T*5 96T*10 96T*100
- FOB
US$ 485
US$ 693
US$ 3119
US$ 5891
US$ 48510
For more details, please contact local distributors!
Specificity
This assay has high sensitivity and excellent specificity for detection of High Sensitive Activated Protein C (APC).
No significant cross-reactivity or interference between High Sensitive Activated Protein C (APC) and analogues was observed.
Recovery
Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of recombinant High Sensitive Activated Protein C (APC) and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of High Sensitive Activated Protein C (APC) in samples.
| Matrix | Recovery range (%) | Average(%) |
| sodium citrate plasma(n=5) | 80-89 | 82 |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, middle and high level High Sensitive Activated Protein C (APC) were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, middle and high level High Sensitive Activated Protein C (APC) were tested on 3 different plates, 8 replicates in each plate.
CV(%) = SD/meanX100
Intra-Assay: CV<10%
Inter-Assay: CV<12%
Linearity
The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of High Sensitive Activated Protein C (APC) and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| Sample | 1:2 | 1:4 | 1:8 | 1:16 |
| sodium citrate plasma(n=5) | 78-97% | 99-105% | 80-103% | 80-96% |
Stability
The stability of kit is determined by the loss rate of activity. The loss rate of this kit is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
To minimize extra influence on the performance, operation procedures and lab conditions, especially room temperature, air humidity, incubator temperature should be strictly controlled. It is also strongly suggested that the whole assay is performed by the same operator from the beginning to the end.
Reagents and materials provided
| Reagents | Quantity | Reagents | Quantity |
| Pre-coated, ready to use 96-well strip plate | 1 | Plate sealer for 96 wells | 4 |
| Standard | 2 | Standard Diluent | 1×20mL |
| Detection Reagent A | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent A | 1×12mL |
| Detection Reagent B | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent B | 1×12mL |
| TMB Substrate | 1×9mL | Stop Solution | 1×6mL |
| Wash Buffer (30 × concentrate) | 1×20mL | Instruction manual | 1 |
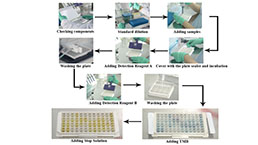
Assay procedure summary
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards;
2. Add 100µL standard or sample to each well. Incubate 1 hours at 37°C;
3. Aspirate and add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent A. Incubate 1 hour at 37°C;
4. Aspirate and wash 3 times;
5. Add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent B. Incubate 30 minutes at 37°C;
6. Aspirate and wash 5 times;
7. Add 90µL Substrate Solution. Incubate 10-20 minutes at 37°C;
8. Add 50µL Stop Solution. Read at 450nm immediately.
GIVEAWAYS
INCREMENT SERVICES
| Magazine | Citations |
| The Journal of Immunology | Activated Protein C Attenuates Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Lupus Nephritis in MRL-Fas(lpr) Mice Jimmunol: 3413 |
| Critical Care | Disseminated intravascular coagulation or acute coagulopathy of trauma shock early after trauma? An observational study BioMed: cc10553 |
| Molecular Endocrinology | Intraovarian Thrombin and Activated Protein C Signaling System Regulates Steroidogenesis during the Periovulatory Period Endo: source |
| Scandinavian Journal of Trauma, Resuscitation and Emergency Medicine | High levels of soluble VEGF receptor 1 early after trauma are associated with shock, sympathoadrenal activation, glycocalyx degradation and inflammation in severely injured patients: a prospective study Sjtrem:1757-7241 |
| Crit Care. | Impact of plasma histones in human sepsis and their contribution to cellular injury and inflammation Pubmed:25260379 |
| Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. | Monocytes regulate systemic coagulation and inflammation in abdominal sepsis Pubmed:25502108 |
| Neuroscience | Protective effects of thrombomodulin on microvascular permeability after subarachnoid hemorrhage in mouse model PubMed: 25936678 |
| Journal of Intensive Care | Activated protein C does not increase in the early phase of trauma with disseminated intravascular coaCavia (Guinea pig )lation: comparison with acute coaCavia (Guinea pig )lopathy of trauma-shock Pubmed:26734467 |
| Journal of Biological Chemistry | Brain microvascular endothelial cells exhibit lower activation of the alternative complement pathway than glomerular microvascular endothelial cells. JBC:Source |
| J Thromb Haemost | A multicenter prospective validation study on disseminated intravascular coagulation in trauma‐induced coagulopathy Pubmed: 32480432 |
| Validation of the Relationship Between Coagulopathy and Localization of Hydroxyethyl Starch on the Vascular Endothelium in a Rat Hemodilution Model 34021192 |
| Catalog No. | Related products for research use of Homo sapiens (Human) Organism species | Applications (RESEARCH USE ONLY!) |
| PAA738Hu01 | Polyclonal Antibody to Activated Protein C (APC) | WB; IHC; ICC; IP. |
| SEA738Hu | ELISA Kit for Activated Protein C (APC) | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Antigen Detection. |
| HEA738Hu | High Sensitive ELISA Kit for Activated Protein C (APC) | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Antigen Detection. |