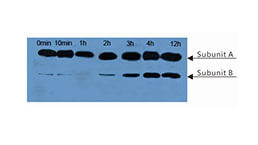
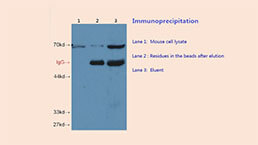
Polyclonal Antibody to Glycated Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c)
Glycosylated Hemoglobin; Hemoglobin A1c; Hb1c; HbAIc; HbAIc
- Product No.PAA190Si01
- Organism SpeciesRhesus monkey (Simian) Same name, Different species.
- SourcePolyclonal antibody preparation
- HostRabbit
- Potencyn/a
- Ig Type IgG
- PurificationAntigen-specific affinity chromatography followed by Protein A affinity chromatography
- LabelNone
- Immunogen NPA190Si01-Native Glycated Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c)
- Buffer Formulation0.01M PBS, pH7.4, containing 0.05% Proclin-300, 50% glycerol.
- TraitsLiquid
- Concentration0.5mg/mL
- Organism Species MoreHomo sapiens (Human), Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
- ApplicationsWB; IHC
If the antibody is used in flow cytometry, please check FCM antibodies. - DownloadInstruction Manual
- UOM 20µl100µl 200µl 1ml 10ml
- FOB
US$ 121
US$ 283
US$ 404
US$ 1010
US$ 4040
For more details, please contact local distributors!
SPECIFITY
The antibody is a rabbit polyclonal antibody raised against HbA1c. It has been selected for its ability to recognize HbA1c in immunohistochemical staining and western blotting.
USAGE
Western blotting: 0.01-2µg/mL;
Immunohistochemistry: 5-20µg/mL;
Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
STORAGE
Store at 4°C for frequent use. Stored at -20°C in a manual defrost freezer for two year without detectable loss of activity. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
STABILITY
The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37°C for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
GIVEAWAYS
INCREMENT SERVICES
| Magazine | Citations |
| J Am Coll Nutr | The Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Glycemic Control and Lipid Profile in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus PubMed: 26391639 |
| Journal of the American College of Nutrition | The Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Glycemic Control and Lipid Profile in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. pubmed:26391639 |
| Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism | Circulating Betatrophin and Hepatocyte Growth Factor in Type 2 Diabetic Patients: Their Relationship With Disease Prognosis 405 |
| Molecular nutrition & food research | Chicory inulin ameliorates type 2 diabetes mellitus and suppresses JNK and MAPK pathways in vivo and in vitro pubmed:28105758 |
| 33 | d-Ribose as a Contributor to Glycated Haemoglobin pubmed:29033370 |
| Journal of Functional Foods | Hypoglycemic effect of Hypericum attenuatum Choisy extracts on type 2 diabetes by regulating glucolipid metabolism and modulating gut microbiota |
| West Indian Medical Journal | Plasma Cellular Hypoxia, Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Disease Risk and Prognostic Factors in Type 2 Diabetic Patients in Saudi Arabia. |
| Journal of Occupational and Environmental Hygiene | Stressors, allostatic load, and health outcomes among women hotel housekeepers: A pilot study Pubmed: 30615593 |
| Cell Reports | Parabacteroides distasonis Alleviates Obesity and Metabolic Dysfunctions via Production of Succinate and Secondary Bile Acids Pubmed: 30605678 |
| Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry | Gymnemic acid alleviates type 2 diabetes mellitus and suppresses endoplasmic reticulum stress in vivo and in vitro |
| Journal of Clinical Medicine | 1H Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)-Based Cerebrospinal Fluid and Plasma Metabolomic Analysis in Type 2 Diabetic Patients and Risk Prediction for Diabetic … Pubmed: 31248127 |
| Food & Function | Gymnemic Acid Alleviates Inflammation and Insulin Resistance via PPARδ-and NFκB-mediated pathways in db/db mice. |
| Obesity Surgery | Duodenal-Jejunal Bypass Ameliorates Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus by Activating Insulin Signaling and Improving Glucose Utilization in the Brain Pubmed: 31605365 |
| Acta Diabetologica | Modulation of gut microbiota contributes to effects of intensive insulin therapy on intestinal morphological alteration in high-fat-diet-treated mice Pubmed: 31749050 |
| Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences | Inhibition of Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products as New Promising Strategy Treatment in Diabetic Retinopathy Pubmed: 32165929 |
| Cell Reports | Activation of a Specific Gut Bacteroides-Folate-Liver Axis Benefits for the Alleviation of Nonalcoholic Hepatic Steatosis Pubmed: 32783933 |
| The effects of different intensity endurance and resistance exercise on diabetic-related blood profiles in impaired glucose tolerance mice | |
| Revista Internacional de Andrologia | Relation of pharmacopenile duplex ultrasonography parameters and glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) in diabetic patients with erectile dysfunction 33334711 |
| Advanced Theory and Simulations? | Identification of Key Contributive Compounds in a Herbal Medicine: A Novel Mathematic¡ªBiological Evaluation Approach |
| Dis Markers | The Roles of Liver Inflammation and the Insulin Signaling Pathway in PM2. 5 Instillation-Induced Insulin Resistance in Wistar Rats 34745386 |
| Antioxidants | Antioxidant Effect of Tyr-Ala Extracted from Zein on INS-1 Cells and Type 2 Diabetes High-Fat-Diet-Induced Mice Pubmed:35740008 |
| P001–Inv. Clínica |
| Catalog No. | Related products for research use of Rhesus monkey (Simian) Organism species | Applications (RESEARCH USE ONLY!) |
| NPA190Si01 | Native Glycated Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) | Positive Control; Immunogen; SDS-PAGE; WB. |
| PAA190Si01 | Polyclonal Antibody to Glycated Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) | WB; IHC |