Packages (Simulation)

Reagent Preparation
Image (I)
Image (II)
Certificate


Mini Samples ELISA Kit for Chemokine (C-X-C Motif) Ligand 2 (CXCL2)
GROb; SCYB2; MIP2; GRO2; MIP2a; MGSAb; CINC2a; HSF; Macrophage inflammatory protein 2-alpha; Hematopoietic synergistic factor; Growth Regulated Oncogene Beta
- Product No.MEB603Mu
- Organism SpeciesMus musculus (Mouse) Same name, Different species.
- Sample Typeserum, plasma, tissue homogenates, cell lysates, cell culture supernates and other biological fluids
- Test MethodDouble-antibody Sandwich
- Assay Length3h
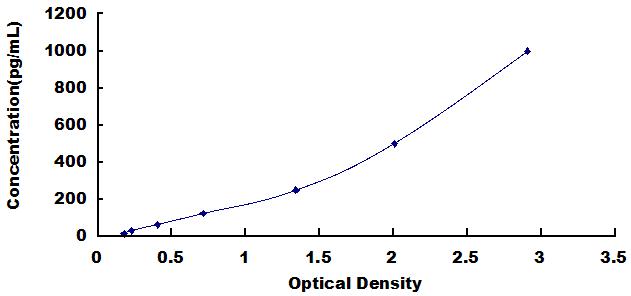
- Detection Range15.6-1,000pg/mL
- SensitivityThe minimum detectable dose of this kit is typically less than 5.5pg/mL.
- DownloadInstruction Manual
- UOM 48T96T 96T*5 96T*10 96T*100
- FOB
US$ 331
US$ 473
US$ 2129
US$ 4021
US$ 33110
For more details, please contact local distributors!
Specificity
This assay has high sensitivity and excellent specificity for detection of Mini Samples Chemokine (C-X-C Motif) Ligand 2 (CXCL2).
No significant cross-reactivity or interference between Mini Samples Chemokine (C-X-C Motif) Ligand 2 (CXCL2) and analogues was observed.
Recovery
Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of recombinant Mini Samples Chemokine (C-X-C Motif) Ligand 2 (CXCL2) and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of Mini Samples Chemokine (C-X-C Motif) Ligand 2 (CXCL2) in samples.
| Matrix | Recovery range (%) | Average(%) |
| serum(n=5) | 91-101 | 94 |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 80-98 | 90 |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 90-104 | 93 |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Mini Samples Chemokine (C-X-C Motif) Ligand 2 (CXCL2) were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Mini Samples Chemokine (C-X-C Motif) Ligand 2 (CXCL2) were tested on 3 different plates, 8 replicates in each plate.
CV(%) = SD/meanX100
Intra-Assay: CV<10%
Inter-Assay: CV<12%
Linearity
The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of Mini Samples Chemokine (C-X-C Motif) Ligand 2 (CXCL2) and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| Sample | 1:2 | 1:4 | 1:8 | 1:16 |
| serum(n=5) | 97-105% | 92-99% | 94-101% | 97-105% |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 83-94% | 95-105% | 86-101% | 93-105% |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 81-90% | 79-102% | 96-105% | 84-101% |
Stability
The stability of kit is determined by the loss rate of activity. The loss rate of this kit is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
To minimize extra influence on the performance, operation procedures and lab conditions, especially room temperature, air humidity, incubator temperature should be strictly controlled. It is also strongly suggested that the whole assay is performed by the same operator from the beginning to the end.
Reagents and materials provided
| Reagents | Quantity | Reagents | Quantity |
| Pre-coated, ready to use 96-well strip plate | 1 | Plate sealer for 96 wells | 4 |
| Standard | 2 | Standard Diluent | 1×20mL |
| Detection Reagent A | 1×60µL | Assay Diluent A | 1×6mL |
| Detection Reagent B | 1×60µL | Assay Diluent B | 1×6mL |
| TMB Substrate | 1×4.5mL | Stop Solution | 1×3mL |
| Wash Buffer (30 × concentrate) | 1×10mL | Instruction manual | 1 |
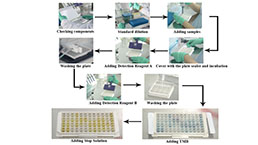
Assay procedure summary
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards;
2. Add 25µL standard or sample to each well. Incubate 1 hour at 37°C;
3. Aspirate and add 25µL prepared Detection Reagent A. Incubate 1 hour at 37°C;
4. Aspirate and wash 3 times;
5. Add 25µL prepared Detection Reagent B. Incubate 30 minutes at 37°C;
6. Aspirate and wash 5 times;
7. Add 25µL Substrate Solution. Incubate 10-20 minutes at 37°C;
8. Add 20µL Stop Solution. Read at 450nm immediately.
GIVEAWAYS
INCREMENT SERVICES
| Magazine | Citations |
| FEBS Journal | Tumour necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced chemokine release in both TRAIL-resistant and TRAIL-sensitive cells via nuclear factor kappa B PubMed: 19120450 |
| PLoS One. | HIF-1α Is Essential for Effective PMN Bacterial Killing, Antimicrobial Peptide Production and Apoptosis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Keratitis Plos: Source |
| Physiol Genomics. | Identification of human exercise-induced myokines using secretome analysis Pubmed:24520153 |
| Diabetes | Protein Inhibitor of Activated STAT 1 (PIAS1) Protects Against Obesity-Induced Insulin Resistance by Inhibiting Inflammation Cascade in Adipose Tissue PubMed: 26324179 |
| Respiration | Bubble CPAP support after discontinuation of mechanical ventilation protects rat lungs with ventilator-induced lung injury Pubmed:26800273 |
| Scientific Reports | The Transcriptional Foundations of Sp110-mediated Macrophage (RAW264. 7) Resistance to Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Ra Pubmed:26912204 |
| Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry | Dexmedetomidine Alleviates HyperoxiaInduced Acute Lung Injury via Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation pubmed:28873369 |
| Medicine (Baltimore) | Rapid detection of urinary soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 for determination of lupus nephritis activity Pubmed:29953010 |
| Hepatology | Integrated Omics Reveals Tollip as an Aggravator and Therapeutic Target for Hepatic Ischemia‐Reperfusion Injury in Mice Pubmed: 31077413 |
| Molecular Medicine Reports | IL‑17A promotes CXCR2‑dependent angiogenesis in a mouse model of liver cancer Pubmed: 31173199 |
| Anticancer Research | The Clinicopathological Significance of the CXCR2 Ligands, CXCL1, CXCL2, CXCL3, CXCL5, CXCL6, CXCL7, and CXCL8 in Gastric Cancer Pubmed: 31810929 |
| Lab Invest | Extracellular cold-inducible RNA-binding protein regulates neutrophil extracellular trap formation and tissue damage in acute pancreatitis Pubmed: 32709888 |
| SCIENCE OF THE TOTAL ENVIRONMENT | Assessment of acute toxicological effects of molybdenum (IV) disulfide nano-and microparticles after single intratracheal administration in rats Pubmed: 32629262 |
| Autophagy | Vitamin D3 and carbamazepine protect against Clostridioides difficile infection in mice by restoring macrophage lysosome acidification Pubmed:34989311 |