Packages (Simulation)

Reagent Preparation
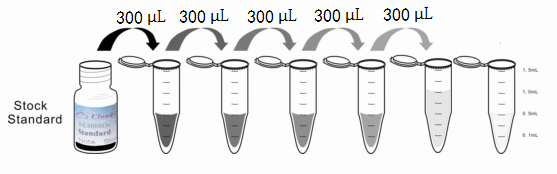
Image (I)
Image (II)
Certificate


Multiplex Assay Kit for Surfactant Protein B (SP-B) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay)
SFTPB; PSPB; SFTB3; SFTP3; SPB; Surfactant Associated Protein B; Pulmonary Surfactant Protein B; 18 kDa pulmonary-surfactant protein; 6 kDa protein
(Note: Up to 8-plex in one testing reaction)
- Product No.LMB622Mu
- Organism SpeciesMus musculus (Mouse) Same name, Different species.
- Sample TypeTissue homogenates, cell lysates, cell culture supernates and other biological fluids
- Test MethodDouble-antibody Sandwich
- Assay Length3.5h
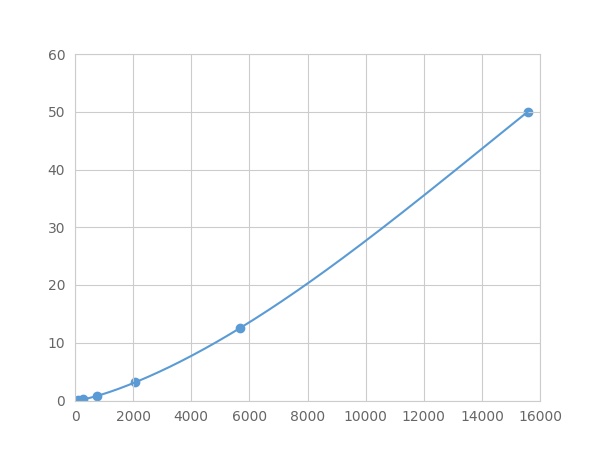
- Detection Range0.05-50ng/mL
- SensitivityThe minimum detectable dose of this kit is typically less than 0.017 ng/mL.
- DownloadInstruction Manual
- UOM 8Plex 7Plex 6Plex 5Plex 4Plex 3Plex 2Plex1Plex
- FOB
US$ 427
US$ 443
US$ 468
US$ 501
US$ 534
US$ 583
US$ 657
US$ 821
Add to Price Calculator
Result
For more details, please contact local distributors!
Specificity
This assay has high sensitivity and excellent specificity for detection of Surfactant Protein B (SP-B) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay).
No significant cross-reactivity or interference between Surfactant Protein B (SP-B) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) and analogues was observed.
Recovery
Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of recombinant Surfactant Protein B (SP-B) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of Surfactant Protein B (SP-B) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) in samples.
| Matrix | Recovery range (%) | Average(%) |
| serum(n=5) | 90-99 | 96 |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 78-96 | 82 |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 87-102 | 91 |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Surfactant Protein B (SP-B) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Surfactant Protein B (SP-B) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) were tested on 3 different plates, 8 replicates in each plate.
CV(%) = SD/meanX100
Intra-Assay: CV<10%
Inter-Assay: CV<12%
Linearity
The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of Surfactant Protein B (SP-B) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| Sample | 1:2 | 1:4 | 1:8 | 1:16 |
| serum(n=5) | 78-102% | 97-104% | 84-95% | 91-99% |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 80-97% | 88-104% | 95-105% | 91-98% |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 86-97% | 88-96% | 80-92% | 93-102% |
Stability
The stability of kit is determined by the loss rate of activity. The loss rate of this kit is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
To minimize extra influence on the performance, operation procedures and lab conditions, especially room temperature, air humidity, incubator temperature should be strictly controlled. It is also strongly suggested that the whole assay is performed by the same operator from the beginning to the end.
Reagents and materials provided
| Reagents | Quantity | Reagents | Quantity |
| 96-well plate | 1 | Plate sealer for 96 wells | 4 |
| Pre-Mixed Standard | 2 | Standard Diluent | 1×20mL |
| Pre-Mixed Magnetic beads (22#:SP-B) | 1 | Analysis buffer | 1×20mL |
| Pre-Mixed Detection Reagent A | 1×120μL | Assay Diluent A | 1×12mL |
| Detection Reagent B (PE-SA) | 1×120μL | Assay Diluent B | 1×12mL |
| Sheath Fluid | 1×10mL | Wash Buffer (30 × concentrate) | 1×20mL |
| Instruction manual | 1 |
Assay procedure summary
1. Preparation of standards, reagents and samples before the experiment;
2. Add 100μL standard or sample to each well,
add 10μL magnetic beads, and incubate 90min at 37°C on shaker;
3. Remove liquid on magnetic frame, add 100μL prepared Detection Reagent A. Incubate 60min at 37°C on shaker;
4. Wash plate on magnetic frame for three times;
5. Add 100μL prepared Detection Reagent B, and incubate 30 min at 37°C on shaker;
6. Wash plate on magnetic frame for three times;
7. Add 100μL sheath solution, swirl for 2 minutes, read on the machine.
GIVEAWAYS
INCREMENT SERVICES
| Magazine | Citations |
| Respiratory Physiology & Neurobiology | Kinetics of plasma SPB and RAGE during mechanical ventilation in patients undergoing major vascular surgery PubMed: 21736957 |
| American Journal of Rhinology & Allergy | Detection of surfactant proteins A, B, C, and D in human nasal mucosa and their regulation in chronic rhinosinusitis with polyps PubMed: 23406594 |
| 19 | Surfactant protein B and RAGE increases in the plasma during cardiopulmonary bypass: a pilot study PubMed: 20650982 |
| Plos one | Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa Express and Secrete Human Surfactant Proteins PubMed: PMC3551896 |
| Plos one | The Detection of Surfactant Proteins A, B, C and D in the Human Brain and Their Regulation in Cerebral Infarction, Autoimmune Conditions and Infections of the CNS PubMed: PMC3787032 |
| Cancer Cell. | Lung Cancer Signatures in Plasma Based on Proteome Profiling of Mouse Tumor Models PubMed: PMC3406925 |
| Respir Physiol Neurobiol | Acute high-altitude exposure reduces lung diffusion: Data from the HIGHCARE Alps project Pubmed: 23619193 |
| PLOS ONE | Surfactant-Derived Proteins as Markers of Alveolar Membrane Damage in Heart Failure Pubmed:25514679 |
| Nachweis und Charakterisierung des Oberfl?chenproteins PLUNC (Palate, Lung and Nasal Clone Protein) an der Augenoberfl?che und Bedeutung für das Trockene Auge Opus4:Source | |
| Int J Cardiol | Plasma immature form of surfactant protein type B correlates with prognosis in patients with chronic heart failure. A pilot single-center prospective study PubMed: 26310985 |
| Plos One | Serum Levels of Surfactant Proteins in Patients with Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema (CPFE) Pubmed:27337142 |
| PLoS One | The Cerebral Surfactant System and Its Alteration in HydrocephalicConditions. pubmed:27656877 |
| Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience | Correlations of Ventricular Enlargement with Rheologically Active SurfactantProteins in Cerebrospinal Fluid. pubmed:28101052 |
| Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience | Correlations of Ventricular Enlargement with Rheologically Active Surfactant Proteins in Cerebrospinal Fluid PMC5209370 |
| Respiratory Physiology & Neurobiology | Diving and pulmonary physiology: surfactant binding protein, lung fluid and cardiopulmonary test changes in professional divers pubmed:28467885 |
| Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry | Surfactant Protein B Suppresses Lung Cancer Progression by Inhibiting Secretory Phospholipase A2 Activity and Arachidonic Acid Production pubmed:28743125 |
| American Journal of Physiology. Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology | Chronic lung injury and impaired pulmonary function in a mouse model of acid ceramidase deficiency. pubmed:29167126 |
| Respiratory research | Effects and molecular mechanisms of intrauterine infection/inflammation on lung development Pubmed:29747649 |
| Respiratory Physiology & Neurobiology | Surfactant proteins changes after acute hemodynamic improvement in patients with advanced chronic heart failure treated with Levosimendan Pubmed:29548887 |
| Lung | Serum Surfactant Protein Levels in Patients Admitted to the Hospital with Acute COPD Exacerbation Pubmed:29445934 |
| American Journal of Physiology Lung Cellular andMolecular Physiology | Generation of an alveolar epithelial type II cell line from induced pluripotent stem cells Pubmed: 30211653 |
| Respiratory Research | Culture of human alveolar epithelial type II cells by sprouting Pubmed: 30340591 |
| Catalog No. | Related products for research use of Mus musculus (Mouse) Organism species | Applications (RESEARCH USE ONLY!) |
| RPB622Mu01 | Recombinant Surfactant Protein B (SP-B) | Positive Control; Immunogen; SDS-PAGE; WB. |
| PAB622Mu01 | Polyclonal Antibody to Surfactant Protein B (SP-B) | WB; IHC |
| LAB622Mu71 | Biotin-Linked Polyclonal Antibody to Surfactant Protein B (SP-B) | IHC |
| SEB622Mu | ELISA Kit for Surfactant Protein B (SP-B) | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Antigen Detection. |
| LMB622Mu | Multiplex Assay Kit for Surfactant Protein B (SP-B) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) | FLIA Kit for Antigen Detection. |