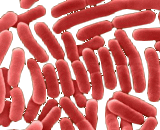
Salmonella enterica is a rod-shaped, flagellated, facultative anaerobic, Gram-negative bacterium and a member of the genus Salmonella. Most cases of salmonellosis are caused by food infected with S. enterica, which often infects cattle and poultry, though other animals such as domestic cats and hamsters have also been shown to be sources of infection in humans. Investigations of vacuum cleaner bags have shown that households can act as a reservoir of the bacterium; this is more likely if the household has contact with an infection sourc. almonella enterica has 7 subspecies, and each subspecies has associated serovars that differ by antigenic specificity. There are over 2500 serovars for S. enterica. Salmonella bongori was previously considered a subspecies of S. enterica, but it is now the other species in the Salmonella genus. Most of the human pathogenic Salmonella serovars belong to the enterica subspecies.