Cloud-Clone Multiplex Assay Kits for Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune disease (AID) refers to the phenomenon where the body's immune system mounts an immune response against its own tissue cells. When such an immune response leads to cellular destruction or tissue damage, accompanied by clinical symptoms, it is termed an autoimmune disease. Any of a group of conditions or disorders that result from immune system malfunction, in which immune components react against the body's own normal cells. Autoimmune diseases are divided into two classes: organ-specific and systemic. An organ-specific disease is one in which an immune response is directed against antigens in a single organ; examples include Addison's disease, in which autoantibodies attack the adrenal cortex, and myasthenia gravis, in which they attack neuromuscular cells. In systemic diseases, the immune system attacks self-antigens in multiple organs. Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), for example, is characterized by inflammation of the skin, joints, kidneys, among with other organs.
The clinical core of autoimmune diseases (e.g., SLE and rheumatoid arthritis) lies in achieving precise diagnosis, activity assessment, and prognosis monitoring through specific antibodies (e.g., anti-dsDNA, rheumatoid factor (RF)) and complement components (C3/C4). Key indicators include: antinuclear antibodies (ANA) for broad-spectrum screening, anti-Sm antibodies (highly specific for SLE), and anti-SSA/SSB antibodies (indicative of Sjögren's syndrome), while cytokines like interleukin-6 (IL-6) dynamically reflect inflammatory status. Testing must integrate multi-dimensional clinical analysis for individualized treatment. Pathological damage and functional impairment are confined to specific organs targeted by antibodies or sensitized lymphocytes, as seen in chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis, Graves' disease, type 1 diabetes mellitus, and myasthenia gravis.
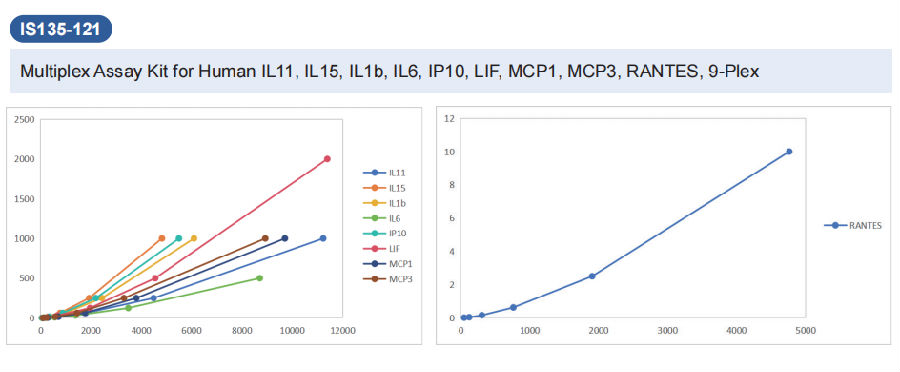
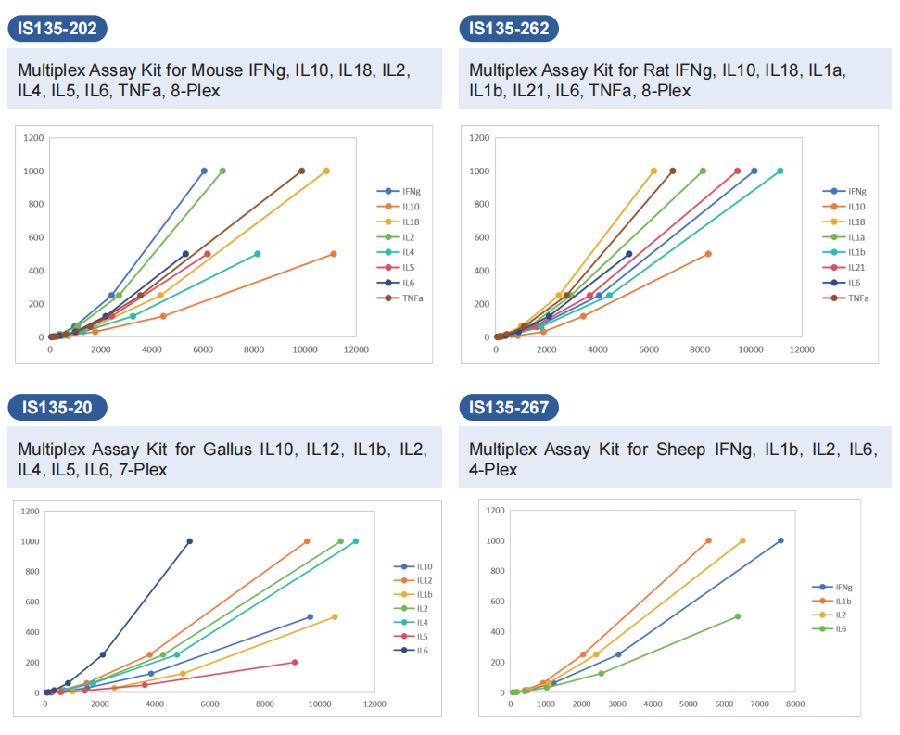
Cloud-Clone Multiplex Assay Kit Detection Cases for Autoimmune Diseases