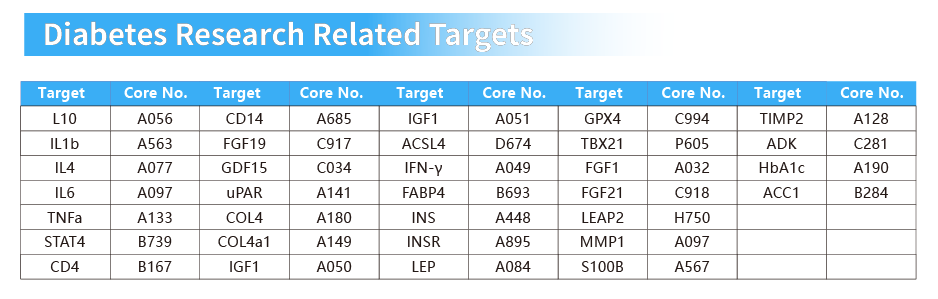
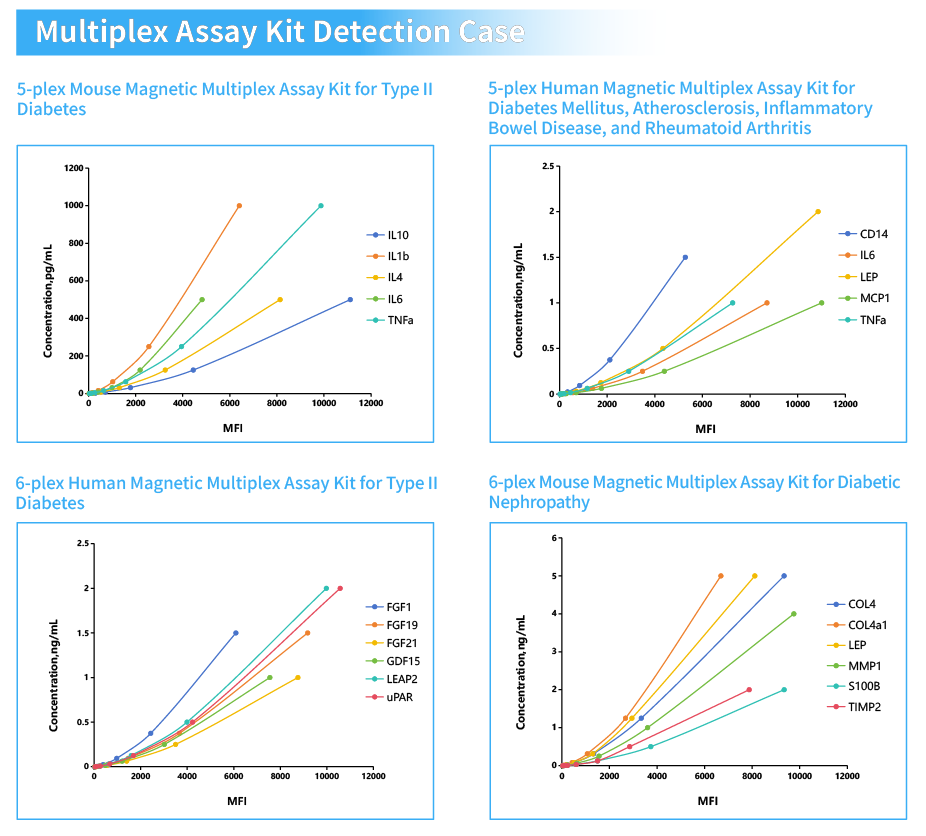
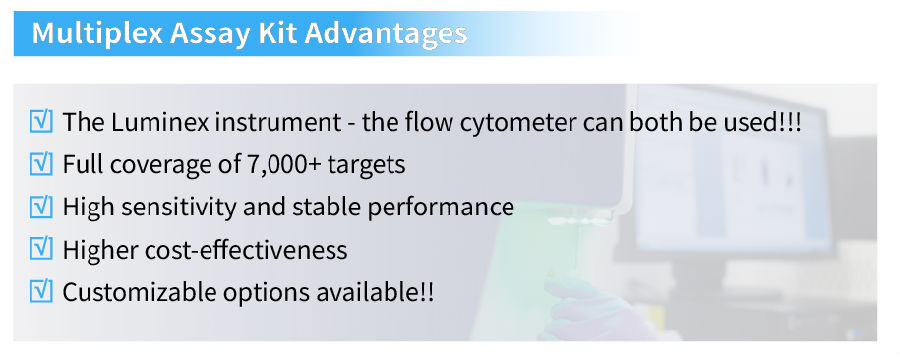
Cloud-Clone Multiplex Assay Kits For Diabetes Research
Diabetes is a serious health problem worldwide. It is caused by chronic high glucose levels in the blood as a result of the incapability of β cells in the pancreas to produce adequate insulin or ineffective insulin utilization by cells in the body. There are generally 3 types of diabetes: Type I, II and gestational diabetes but more emphasis is placed on the first 2 types of diabetes. As a chronic condition, diabetes tends to increase the risk of several other diseases caused by macrovascular and microvascular damage, and it has negative impacts on several organs, such as the brain, kidney, heart, and eyes. In addition, diabetic patients are more susceptible to infection.
Insulin is a protein hormone secreted by the beta cells of the pancreatic islets, often hailed as the "central steward" of blood glucose regulation. It maintains blood glucose stability primarily through two mechanisms: first, by promoting the uptake of glucose into liver, muscle, and adipose tissues, where it is converted into glycogen for storage; second, by inhibiting hepatic gluconeogenesis (the process by which the liver converts non-carbohydrate substances into glucose). For insulin to exert its effects, it must first bind to its "receiver" on the cell surface—the insulin receptor (INSR). The insulin receptor is a transmembrane protein composed of two subunits, α and β. Upon binding, it activates multiple downstream signaling pathways within the cell, with the PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK pathways being the two most critical.