A vaccine-based nanosystem for initiating innate immunity and improving tumor immunotherapy

On April 24, 2020, professor Xian-Zheng Zhang from Key Laboratory of Biomedical Polymers of Ministry of Education & Department of Chemistry of Wuhan University published a paper titled A vaccine-based nanosystem for initiating innate immunity and improving tumor immunotherapy on Nature communications.
The ELISA kit (MIP1a, SEA092Mu; HA, CEA927Ge) of Cloud-Clone brand was chosed to determine the concentation of MIP1a and HA in this article, we are so proud for supporting the reaserchers.


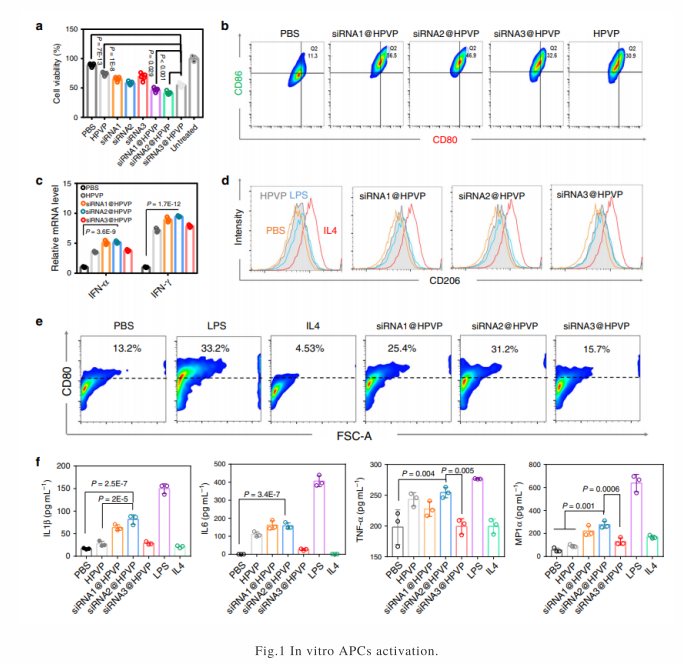
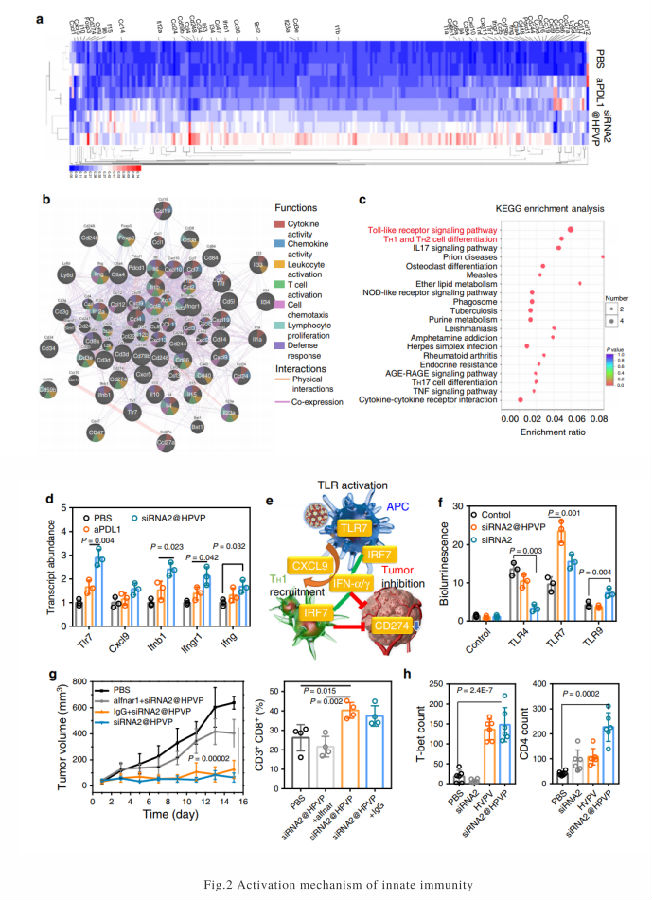
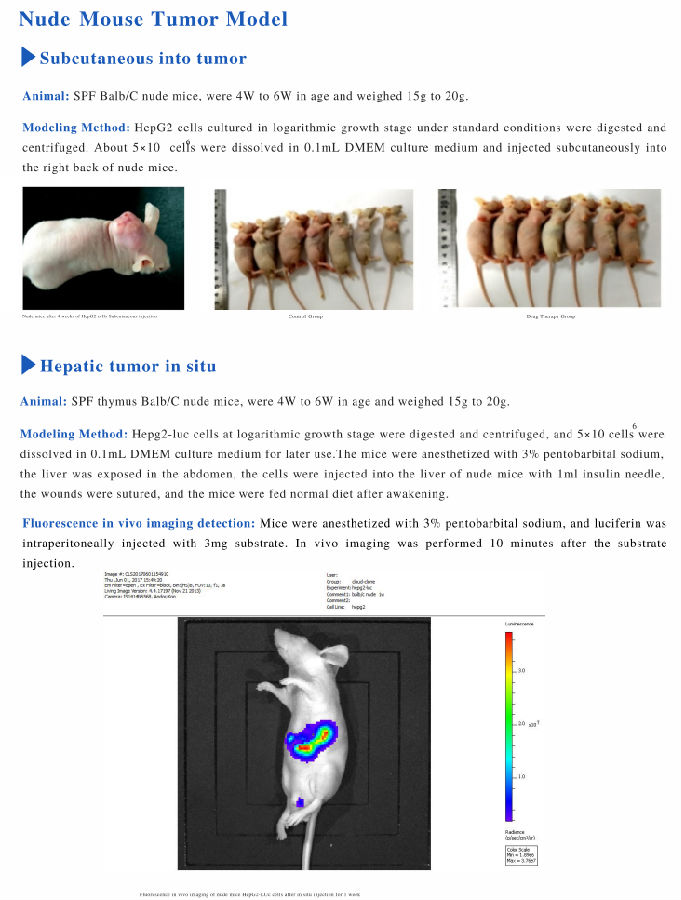
The unsatisfactory response rate of immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) immunotherapy severely limits its clinical application as a tumor therapy. Here, we generate a vaccine-based nanosystem by integrating siRNA for Cd274 into the commercial human papillomavirus (HPV) L1 (HPV16 L1) protein. This nanosystem has good biosafety and enhances the therapeutic response rate of anti-tumor immunotherapy. The HPV16 L1 protein activates innate immunity through the type I interferon pathway and exhibits an efficient anti-cancer effect when cooperating with ICB therapy. For both resectable and unresectable breast tumors, the nanosystem decreases 71% tumor recurrence and extends progression-free survival by 67%. Most importantly, the nanosystem successfully induces high response rates in various genetically modified breast cancer models with different antigen loads. The strong immune stimulation elicited by this vaccine-based nanosystem might constitute an approach to significantly improve current ICB immunotherapy.