Rat Model for Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SH)
SAH
- Product No.DSI691Ra02
- Organism SpeciesRattus norvegicus (Rat) Same name, Different species.
- Prototype SpeciesHuman
- SourceInjection of autogenous blood into cistern magna
- Model Animal StrainsSD Rats(SPF), healthy, male, body weight 180g~200g.
- Modeling GroupingRandomly divided into six group: Control group, Model group, Positive drug group and Test drug group.
- Modeling Period4-6 weeks
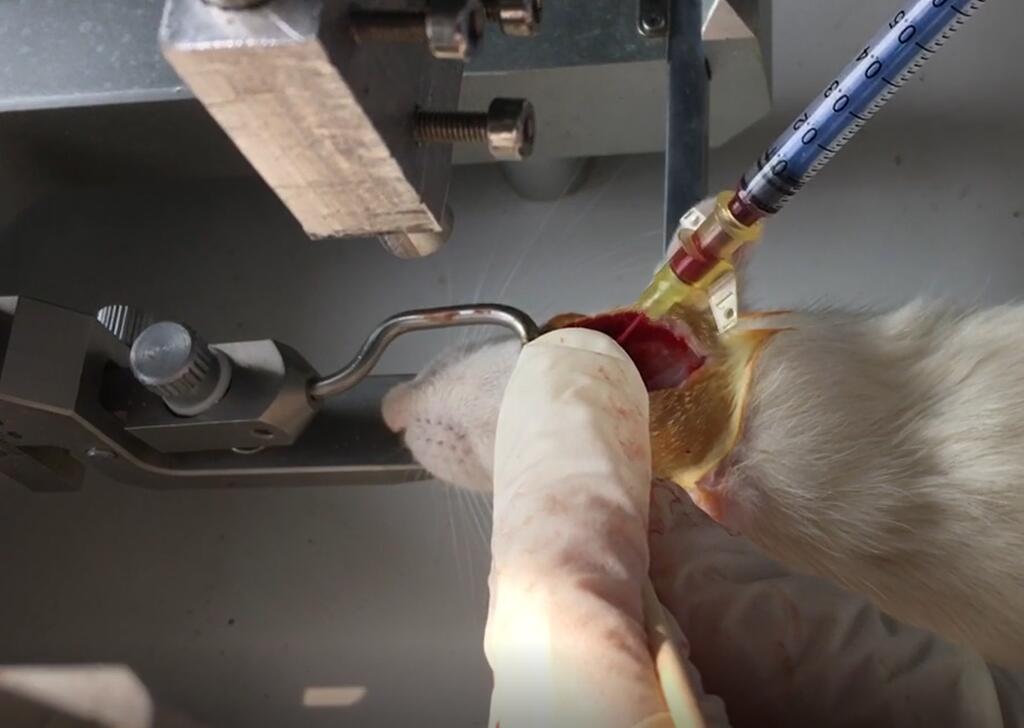
- Modeling MethodAfter weighing, the rats were subjected to abdominal anesthesia. After the anesthesia, the hair on the top of the cranium was shaved, and the animals' heads were fixed on the brain stereolocator to maintain the horizontal position of the cranium.Surgical area disinfection, along the median sagittal line of the skull incision about 2cm long skin, blunt separation of muscle and periosteum, hydrogen peroxide disinfection and hemodialysis, 6mm before the hypergrowing midline, 2~3cm next to the midline, with 5mL syringe needle drilling, surgical microscope with no. 4 needle carefully punctured meninges, see clear cerebrospinal fluid outflow,The catheter was inserted forward at an oblique Angle of 30° in the sagittal plane until the tip reached the base of the anterior cranial fossa at a depth of about 1.0cm from the brain surface.The bone holes were sealed with bone wax.After connecting the syringe and gently aspirating, clear cerebrospinal fluid was seen flowing out, which was confirmed to enter the subarachnoid space.After local disinfection, the rat tail about 2cm long was cut off, and 300μL of rat tail arterial blood was quickly collected and injected into the subarachnoid space with microinjection for 20 seconds.The catheter was pulled out, the bone hole was sealed with medical bio-glue, the skin was sutured layer by layer, and the skin was placed in an incubator.After anesthesia, the rats were put back into the cage for feeding and observation.
- ApplicationsDisease Model
- Downloadn/a
- UOM Each case
- FOB
US$ 260
For more details, please contact local distributors!
Model Evaluation
1.General observation
The hematocele/blood clot around brain surface of rats in each group were observed.
2. Neurocognitive function score
The behavioral scores of Kaoutzanis et al were evaluated 48h after injury.
Eating conditions: 2 points for eating freely, 1 point for refusing to eat;
Motor response: free walking 5 points, difficulty walking 4 points, unable to walk 3 points.
Tingling reaction: 2 points for limb contraction when tingling, 1 point for no reaction when tingling;
Eye-opening reaction: 4 points for self-opening, 3 points for sound stimulation, 2 points for stabbing pain, and 1 point for inability to open eyes.
3. Physiological detection
Changes in the blood-brain barrier were measured.
Blood brain barrier permeability measurement:
(1) The content of Ewan's blue (EB) in brain tissue was determined by zhou Yonggang et al.
First, a standard regression curve was established. EB 10mg was dissolved in 100mL normal saline, 0.1ml was added to 1.9ml formamide and mixed as the first tube, then 0.1ml was added to 1.9ml formamide and mixed as the second tube, 1mL was successively added to 1ml formamide and mixed as the third tube, and so on, a total of 6 tubes were made. 37℃ water bath for 48h, fluorescence spectrophotometer at 610nm for colorimetry, distilled water as blank. EB content in brain tissue was calculated according to the formula: EB content in brain tissue (μg/g brain tissue) : A× formamide amount (mL) ÷ wet weight of brain (g) (A is the EB content of the sample obtained according to the regression equation of the standard curve, in ng/mg).
(2) The rats in each group were injected 2% Evans blue (EB) 2mL /kg through femoral vein one hour before death. In order to remove dye from blood, normal saline was injected into left ventricle with puncture needle until clear and transparent fluid was released from right ventricle.
The brain tissue of the basal temporal cortex of rats was taken by rapid craniotomy and weighed, and the sample was put into a homogenizer containing 1.5mL of 50%TCA solution for homogenization and centrifugation (10000r/min, 20min). 1.0mL of supernatant was taken and 1.5mL of mixture (prepared by 50%TCA and anhydrous ethanol at the ratio of 1:3).Mix well for testing.
Pathological Results
4. HE staining: 48h after modeling, brain tissue and cortical tissue around blood clot were taken from the rats under abdominal anesthesia immediately to observe the damage of brain tissue in each group, and sections were taken for panoramic scanning.
5. Immunohistochemistry: MbL-C antibody was used to detect the cortical tissue around the blood clot, and panoramic scanning was performed in sections.
6. TUNEL test: the cerebral cortex tissues around blood clots were collected to detect the apoptosis of tissue cells after subarachnoid hemorrhage in each group.Section for fluorescence panoramic scanning.
7. WB detection of protein expression: The expression levels of McL-2, C3, TLR4, P65 and P-P65 were detected from the cortical tissues around blood clots.
Cytokines Level
Statistical Analysis
SPSS software is used for statistical analysis, measurement data to mean ± standard deviation (x ±s), using t test and single factor analysis of variance for group comparison, P<0.05 indicates there was a significant difference, P<0.01 indicates there are very significant differences.
GIVEAWAYS
INCREMENT SERVICES
-
 Tissue/Sections Customized Service
Tissue/Sections Customized Service
-
 Serums Customized Service
Serums Customized Service
-
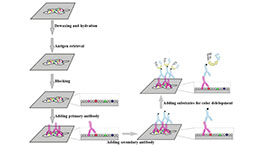 Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Experiment Service
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Experiment Service
-
 Small Animal In Vivo Imaging Experiment Service
Small Animal In Vivo Imaging Experiment Service
-
 Small Animal Micro CT Imaging Experiment Service
Small Animal Micro CT Imaging Experiment Service
-
 Small Animal MRI Imaging Experiment Service
Small Animal MRI Imaging Experiment Service
-
 Small Animal Ultrasound Imaging Experiment Service
Small Animal Ultrasound Imaging Experiment Service
-
 Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Experiment Service
Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Experiment Service
-
 Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Experiment Service
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Experiment Service
-
 Learning and Memory Behavioral Experiment Service
Learning and Memory Behavioral Experiment Service
-
 Anxiety and Depression Behavioral Experiment Service
Anxiety and Depression Behavioral Experiment Service
-
 Drug Addiction Behavioral Experiment Service
Drug Addiction Behavioral Experiment Service
-
 Pain Behavioral Experiment Service
Pain Behavioral Experiment Service
-
 Neuropsychiatric Disorder Behavioral Experiment Service
Neuropsychiatric Disorder Behavioral Experiment Service
-
 Fatigue Behavioral Experiment Service
Fatigue Behavioral Experiment Service
-
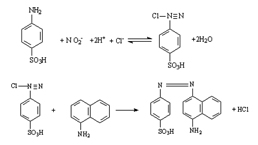 Nitric Oxide Assay Kit (A012)
Nitric Oxide Assay Kit (A012)
-
 Nitric Oxide Assay Kit (A013-2)
Nitric Oxide Assay Kit (A013-2)
-
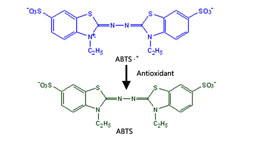 Total Anti-Oxidative Capability Assay Kit(A015-2)
Total Anti-Oxidative Capability Assay Kit(A015-2)
-
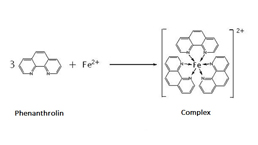 Total Anti-Oxidative Capability Assay Kit (A015-1)
Total Anti-Oxidative Capability Assay Kit (A015-1)
-
 Superoxide Dismutase Assay Kit
Superoxide Dismutase Assay Kit
-
 Fructose Assay Kit (A085)
Fructose Assay Kit (A085)
-
 Citric Acid Assay Kit (A128 )
Citric Acid Assay Kit (A128 )
-
 Catalase Assay Kit
Catalase Assay Kit
-
 Malondialdehyde Assay Kit
Malondialdehyde Assay Kit
-
 Glutathione S-Transferase Assay Kit
Glutathione S-Transferase Assay Kit
-
 Microscale Reduced Glutathione assay kit
Microscale Reduced Glutathione assay kit
-
 Glutathione Reductase Activity Coefficient Assay Kit
Glutathione Reductase Activity Coefficient Assay Kit
-
 Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Kit
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Kit
-
 Glutathione Peroxidase (GSH-PX) Assay Kit
Glutathione Peroxidase (GSH-PX) Assay Kit
-
 Cloud-Clone Multiplex assay kits
Cloud-Clone Multiplex assay kits
| Catalog No. | Related products for research use of Rattus norvegicus (Rat) Organism species | Applications (RESEARCH USE ONLY!) |
| DSI691Ra01 | Rat Model for Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SH) | n/a |
| DSI691Ra02 | Rat Model for Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SH) | Disease Model |
| TSI691Ra15 | Rat Brain Tissue of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SH) | Paraffin slides for pathologic research: IHC,IF and HE,Masson and other stainings |