Packages (Simulation)

Reagent Preparation
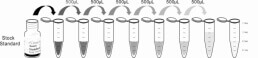
Image (I)
Image (II)
Certificate


ELISA Kit for Cytochrome C (CYCS)
Cyt-C; HCS; CYC; CytC
- Product No.SEA594Po
- Organism SpeciesSus scrofa; Porcine (Pig) Same name, Different species.
- Sample TypeTissue homogenates, cell lysates, cell culture supernates and other biological fluids
- Test MethodDouble-antibody Sandwich
- Assay Length3h
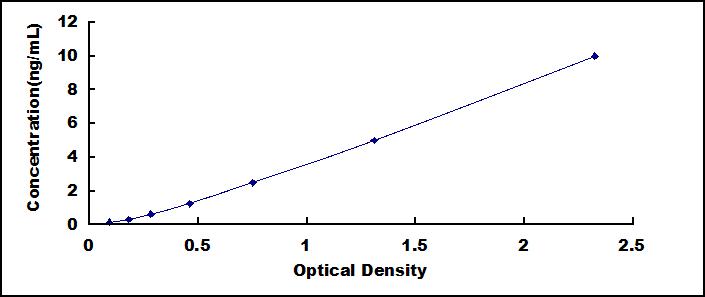
- Detection Range0.156-10ng/mL
- SensitivityThe minimum detectable dose of this kit is typically less than 0.062ng/mL.
- DownloadInstruction Manual
- UOM 48T96T 96T*5 96T*10 96T*100
- FOB
US$ 529
US$ 756
US$ 3402
US$ 6426
US$ 52920
For more details, please contact local distributors!
Specificity
This assay has high sensitivity and excellent specificity for detection of Cytochrome C (CYCS).
No significant cross-reactivity or interference between Cytochrome C (CYCS) and analogues was observed.
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Cytochrome C (CYCS) were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Cytochrome C (CYCS) were tested on 3 different plates, 8 replicates in each plate.
CV(%) = SD/meanX100
Intra-Assay: CV<10%
Inter-Assay: CV<12%
Stability
The stability of kit is determined by the loss rate of activity. The loss rate of this kit is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
To minimize extra influence on the performance, operation procedures and lab conditions, especially room temperature, air humidity, incubator temperature should be strictly controlled. It is also strongly suggested that the whole assay is performed by the same operator from the beginning to the end.
Reagents and materials provided
| Reagents | Quantity | Reagents | Quantity |
| Pre-coated, ready to use 96-well strip plate | 1 | Plate sealer for 96 wells | 4 |
| Standard | 2 | Standard Diluent | 1×20mL |
| Detection Reagent A | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent A | 1×12mL |
| Detection Reagent B | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent B | 1×12mL |
| TMB Substrate | 1×9mL | Stop Solution | 1×6mL |
| Wash Buffer (30 × concentrate) | 1×20mL | Instruction manual | 1 |
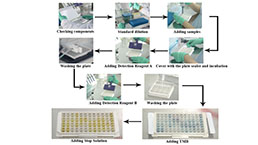
Assay procedure summary
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards;
2. Add 100µL standard or sample to each well. Incubate 1 hours at 37°C;
3. Aspirate and add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent A. Incubate 1 hour at 37°C;
4. Aspirate and wash 3 times;
5. Add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent B. Incubate 30 minutes at 37°C;
6. Aspirate and wash 5 times;
7. Add 90µL Substrate Solution. Incubate 10-20 minutes at 37°C;
8. Add 50µL Stop Solution. Read at 450nm immediately.
GIVEAWAYS
INCREMENT SERVICES
-
 Single-component Reagents of Assay Kit
Single-component Reagents of Assay Kit
-
 Lysis Buffer Specific for ELISA / CLIA
Lysis Buffer Specific for ELISA / CLIA
-
 Quality Control of Kit
Quality Control of Kit
-
 ELISA Kit Customized Service
ELISA Kit Customized Service
-
 Disease Model Customized Service
Disease Model Customized Service
-
 Serums Customized Service
Serums Customized Service
-
 TGFB1 Activation Reagent
TGFB1 Activation Reagent
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
-
 Streptavidin
Streptavidin
-
 Fast blue Protein Stain solution
Fast blue Protein Stain solution -
 Single-component Reagents of FLIA Kit
Single-component Reagents of FLIA Kit
-
 Streptavidin-Agarose Beads
Streptavidin-Agarose Beads
| Magazine | Citations |
| J Ethnopharmacol | Danhong injection protects cardiomyocytes against hypoxia/reoxygenation- and H2O2-induced injury by inhibiting mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening PubMed: 26320687 |
| Cell Stress Chaperones | Gypenosides alleviate myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via attenuation of oxidative stress and preservation of mitochondrial function in rat heart Pubmed:26800973 |
| Molecules | Clematichinenoside (AR) Attenuates Hypoxia/Reoxygenation-Induced H9c2 Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis via a Mitochondria-Mediated Signaling Pathway Pubmed:27248986 |
| International Journal of Biological Macromolecules | A polysaccharide (PNPA) from Pleurotus nebrodensis ameliorates hepatic ischemic/reperfusion (I/R) injury in rats pubmed:28709897 |
| West Indian Medical Journal | Plasma Cellular Hypoxia, Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Disease Risk and Prognostic Factors in Type 2 Diabetic Patients in Saudi Arabia. |
| PeerJ. | Taxifolin protects rat against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by modulating the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway Pubmed: 30723634 |
| Biological trace element research | High Concentrations of Boric Acid Trigger Concentration-Dependent Oxidative Stress, Apoptotic Pathways and Morphological Alterations in DU-145 Human Prostate … Pubmed: 31066018 |
| Biological Trace Element Research | The Role of Oxidative Stress, Renal Inflammation, and Apoptosis in Post Ischemic Reperfusion Injury of Kidney Tissue: the Protective Effect of Dose-Dependent Boric … |
| Cell Stress Chaperones | Betaine suppresses cell proliferation by increasing oxidative stress–mediated apoptosis and inflammation in DU-145 human prostate cancer cell line Pubmed: 31368044 |
| Biological trace element research | Concentration-Dependent Effects of Zinc Sulfate on DU-145 Human Prostate Cancer Cell Line: Oxidative, Apoptotic, Inflammatory, and Morphological Analyzes Pubmed: 31463762 |
| Life Sciences | Curcumin and LOXblock-1 ameliorate ischemia-reperfusion induced inflammation and acute kidney injury by suppressing the semaphorin-plexin pathway. Pubmed: 32603817 |
| J Biochem Mol Toxicol | Concanavalin A induces apoptosis in a dose©\dependent manner by modulating thiol/disulfide homeostasis in C6 glioblastoma cells 33604990 |
| Reprod Sci | Reproductive Effects of Nicotinamide on Testicular Function and Structure in Old Male Rats: Oxidative, Apoptotic, Hormonal, and Morphological Analyses 34101148 |
| Environ Sci Pollut Res Int | Comparative effects of metformin and Cistus laurifolius L. extract in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat model: oxidative, inflammatory, apoptotic, and histopathological?¡ 34097215 |
| Biomed Pharmacother | Allicin ameliorates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury via inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation in rats 34426252 |
| Redox Biol | 12/15–Lipoxygenase debilitates mitochondrial health in intermittent hypobaric hypoxia induced neuronal damage: An in vivo study Pubmed:34979449 |
| Cancers (Basel) | In Vivo and In Vitro Enhanced Tumoricidal Effects of Metformin, Active Vitamin D3, and 5-Fluorouracil Triple Therapy against Colon Cancer by Modulating the … Pubmed:35326689 |
| Cell Death & Disease | Proteomic analysis reveals USP7 as a novel regulator of palmitic acid-induced hepatocellular carcinoma cell death Pubmed:35732625 |
| Journal of Nanobiotechnology | Microbial hydrogen “manufactory” for enhanced gas therapy and self-activated immunotherapy via reduced immune escape Pubmed:35705974 |
| Value Health Sci | Oksidatif, Apoptotik ve İnflamatuar Sinyal Yolakları üzerinden C6 Glioblastoma Hücrelerindeki ML351'in Antiproliferatif Etkileri |
| Metformin and Calcitriol Enhance 5-Fluorouracil Tumoricidal Effects in Colon Cancer By Modulating The PI3K/Akt/PTEN/mTOR Network |
| Catalog No. | Related products for research use of Sus scrofa; Porcine (Pig) Organism species | Applications (RESEARCH USE ONLY!) |
| NPA594Po01 | Native Cytochrome C (CYCS) | Positive Control; Immunogen; SDS-PAGE; WB. |
| SEA594Po | ELISA Kit for Cytochrome C (CYCS) | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Antigen Detection. |
| LMA594Po | Multiplex Assay Kit for Cytochrome C (CYCS) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) | FLIA Kit for Antigen Detection. |